Table of Contents
Zinc finger motif is zinc-coordinated DNA-binding motif. The types, structures and the examples are described here. This is the part of molecular biology, important for all Life Science related competitive examinations.
Types:
There are several types of zinc finger motifs. The most widely occurring (the most common type) zinc finger motif in eukaryotes is the Cys2-His2 (C2-H2) zinc finger, which was the first discovered in a transcription factor called TFIIIA that controls the transcription of genes for 5S rRNA.
Cys2-His2 (C2-H2) zinc finger motif:
This class of zinc fingers occurs in clusters. Each finger is approximately 30 amino acids long and is characterized by pairs of Cys and His that always occur at the same relative positions.
The consensus sequence of a single finger is:
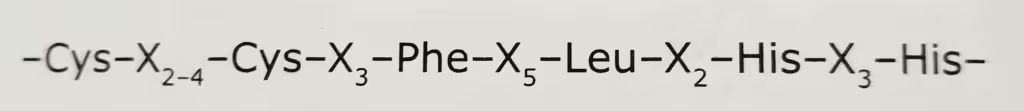
The importance of zinc as ionic form in this type of DNA-binding motif :
It forms a compact, globular domain in which a zinc ion is coordinated tetrahedrally by the Cys and His residues. The zinc is essential for correct folding and DNA binding.
The NMR and X-ray studies of Cys2-His2 (C2-H2) zinc finger motif:
- NMR and X-ray studies have shown that the C2-H2 finger is a compact globular domain.
- It is composed of a 12 residue α helix packed against an irregular β sheet, with the zinc in between.
- The α helix of each finger lies in the major groove and contacts three base pairs.
- The base contacts are almost entirely with one DNA strand.
The Zinc-coordinated DNA-binding motifs- as steroid receptors:
A second class of DNA -binding domain that makes structural use of of zinc is found in the steroid receptors. Steroid receptors are activators. The DNA-binding domain of a steroid receptor is a type of zinc finger that has a cys, but no his residues.
The DNA-binding domains of these factors are 70-80 amino acids long and contain two zinc ions, each coordinated tetrahedrally with four Cys residues. They are therefore referred to as Cys2-Cys2 (C2-C2) zinc fingers.
The Zn binding consensus sequence of C2-C2 zinc finger motif is given below:
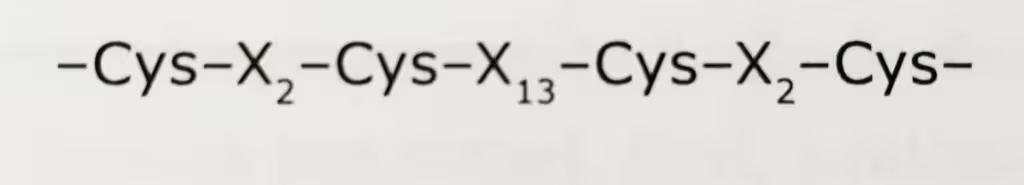
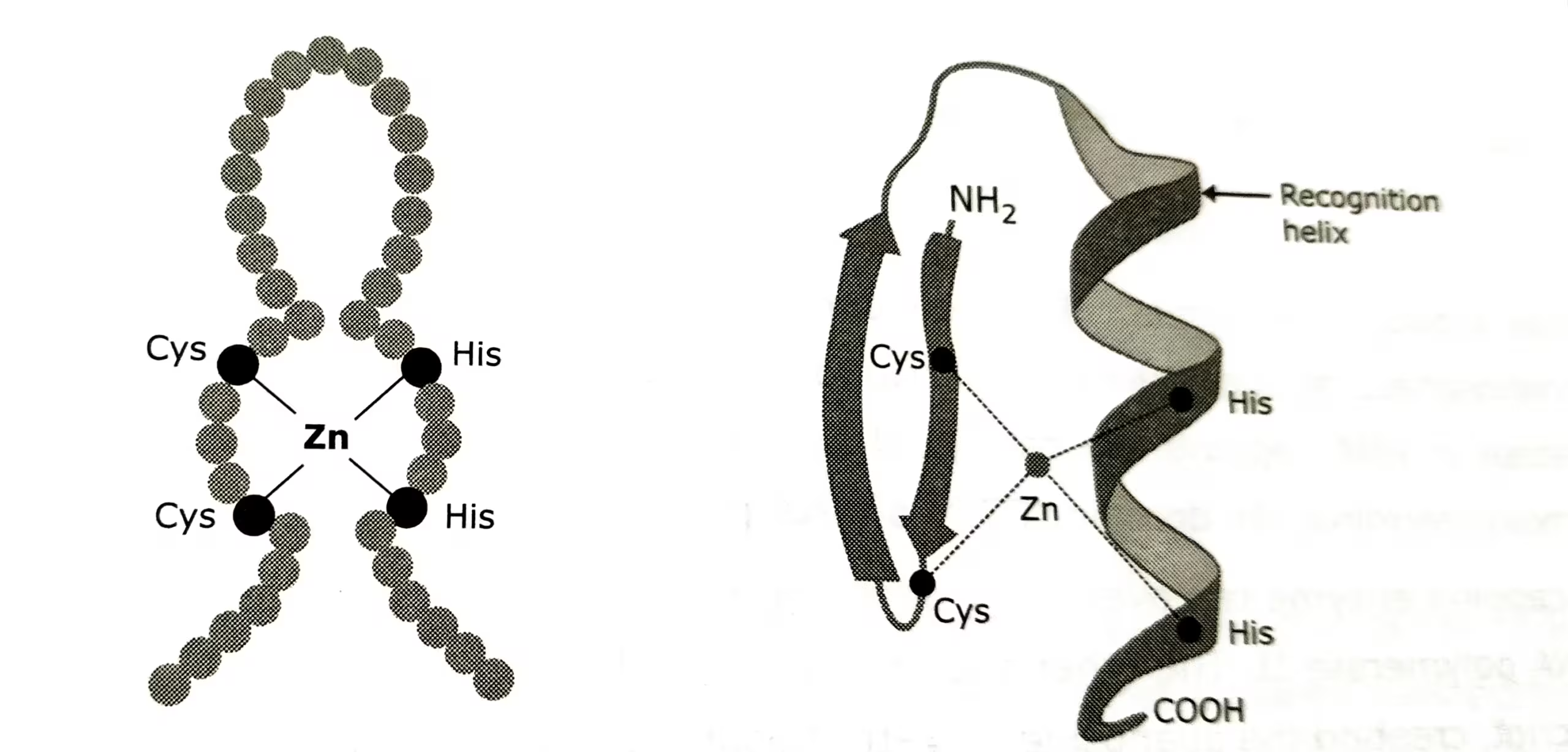
The diagrammatic representation of (C2-H2) zinc finger :
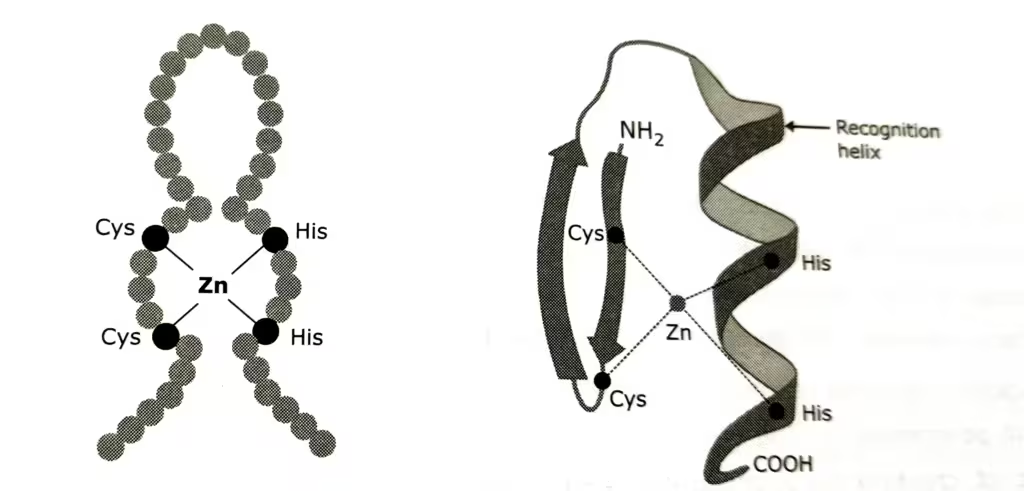
The description of above diagram:
The C2-H2 zinc finger is the common DNA-binding motif. The motif has a 23-to 26-residue consensus sequence containing two conserved Cys and two conserved His residues, whose side chains bind one zinc ion. The name zinc finger was coined because a two-dimensional diagram of the structure resembles a finger. When the three dimensional structure was solved, it became clear that the binding of the zinc ion by the two cysteine and two histidine residues folds the relatively short polypeptide sequence into a compact domain.
Examples of transcription regulatory proteins that contain the zinc finger motif:
| Binding motif | Organism | Regulatory protein |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc finger | Yeast | Gal 4 |
| Zinc finger | Xenopus | TFIIIA |
| Zinc finger | Mammals | Receptors of steroid hormones |
Other DNA binding motifs:
- Introduction to DNA binding motifs: https://thebiologyislove.com/dna-binding-motifs/
- helix-turn-helix: https://thebiologyislove.com/helix-turn-helix-motif/
- helix-loop-helix: https://thebiologyislove.com/helix-loop-helix-motif/
- Leucine zipper motif: https://thebiologyislove.com/leucine-zipper-motif/
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/J2qrsLcgMDowyrSS/?mibextid=oFDknk
Instagram Link: https://www.instagram.com/reel/C8l-iB1RIgS/?igsh=bXkydDEwbWUzaDZx