Table of Contents
The term ‘population growth’ refers to the change in the number of individuals in a population with time. It refers to how the number of individuals in a population increases or decreases with time.
Population growth- Introduction:
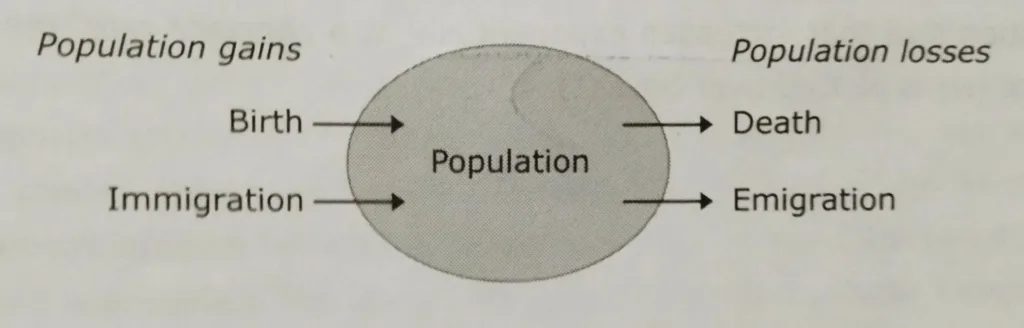
Population change is determined by four factors: birth, death, emigration, and immigration.
In a closed population, change in population is only related to birth and death of individuals.
In case of open population, birth, death, immigration and emigration result in a change of population.
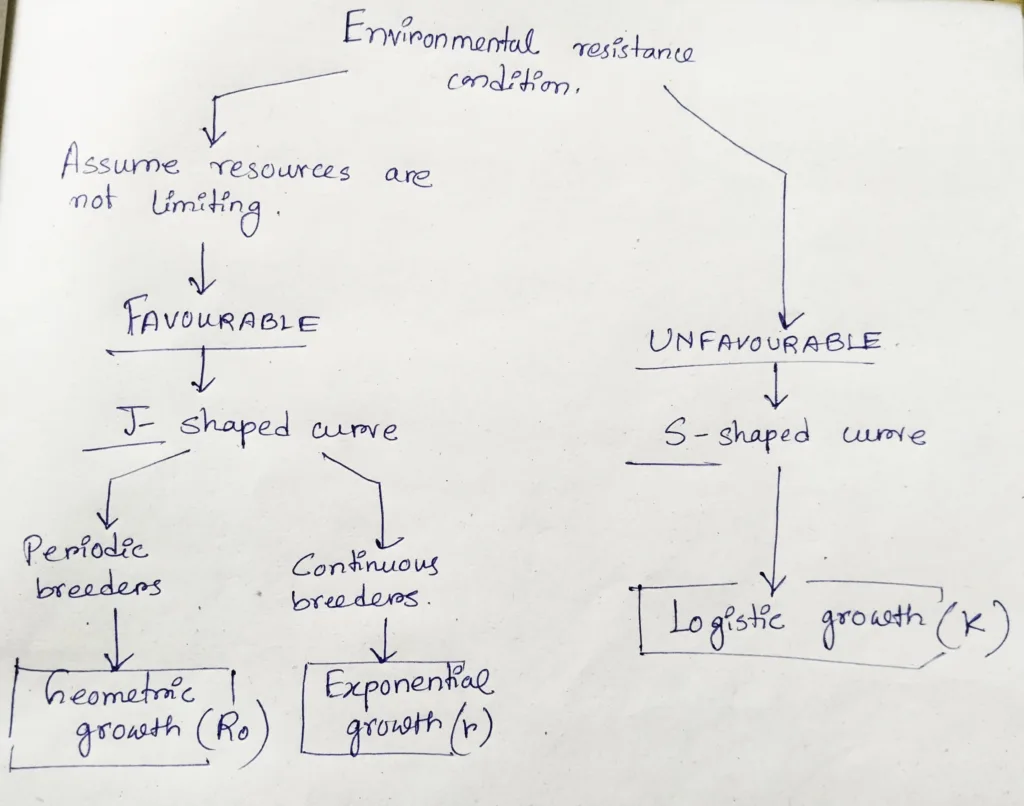
There are two types of environmental resistance conditions. One is favorable (unlimited resources) and the other one is unfavorable. Under favorable condition there are two types of growth- 1) geometric growth, 2) Exponential growth. Under unfavorable condition there is logistic growth.
Exponential Growth – explanation
For some organisms, such as bacteria, internal parasites, some insects, or humans, reproduction can be continuous. Exponential growth describes population growth for continuous breeders. Based on hypothesis that the resources are unlimited.
The change in population size over any time period can be written as the number of births per unit time interval minus the number of deaths per unit time interval.

r= intrinsic rate of increase
- During exponential population growth under an ideal unlimited environment, per capita rate of increase is maximum and is called the intrinsic rate of increase (or instantaneous rate of increase).
- The maximum value of r is often referred by the less specific but widely used expression biotic potential (or reproductive potential). It is the maximum per capita growth rate in the absence of environmental resistance.
- The sum total of all environment factors that together act to limit the biotic potential of an organism from being realized is called environment resistance. It includes both biotic factors ( such as predation, competition, parasitism) and abiotic factors ( such as drought, fire, flood etc.).
- Biotic potential differs from one species to another—example: Mice or deer populations cam grow faster than a population of elephants.
The equations of exponential growth:
All members have abundant resource availability and the population display it’s intrinsic rate of increase. Maximum number of offspring born per individual. This form of growth is represented by:
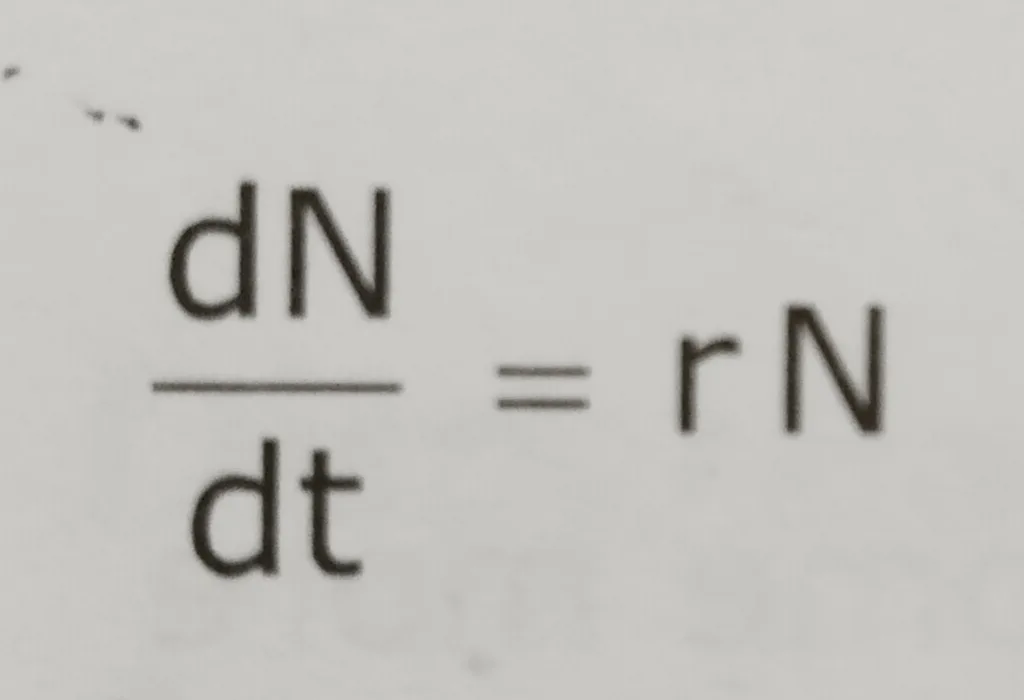
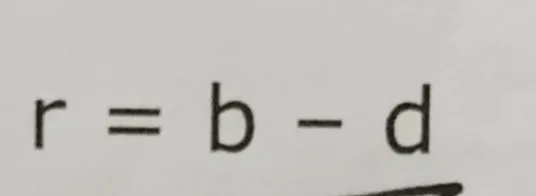
Where,
N= population size
r= intrinsic rate of increase, or , maximum potential to reproduce (in unlimited resource condition) or per capita growth rate/ growth rate constant or Biotic potential
b= per capita birth rate
d= per capita death rate
In nature population may grow exponentially for some period of time, but there will be a limitation of resources after some time.
The integral form of the exponential growth is-
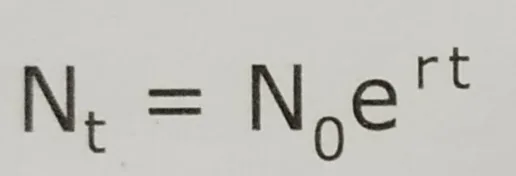
Nt= population density at time t
N0= population density at time 0
r= intrinsic rate of natural increase
t= time interval
e= the base of natural logarithm (constant about 2.7)
The term e to the power r is the factor by which the population increases during each time unit
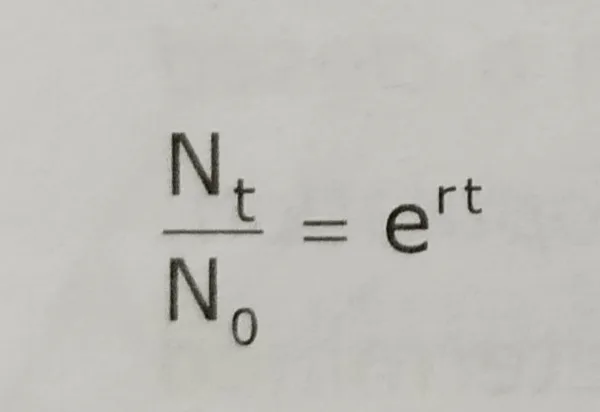
By taking the natural log of both sides,

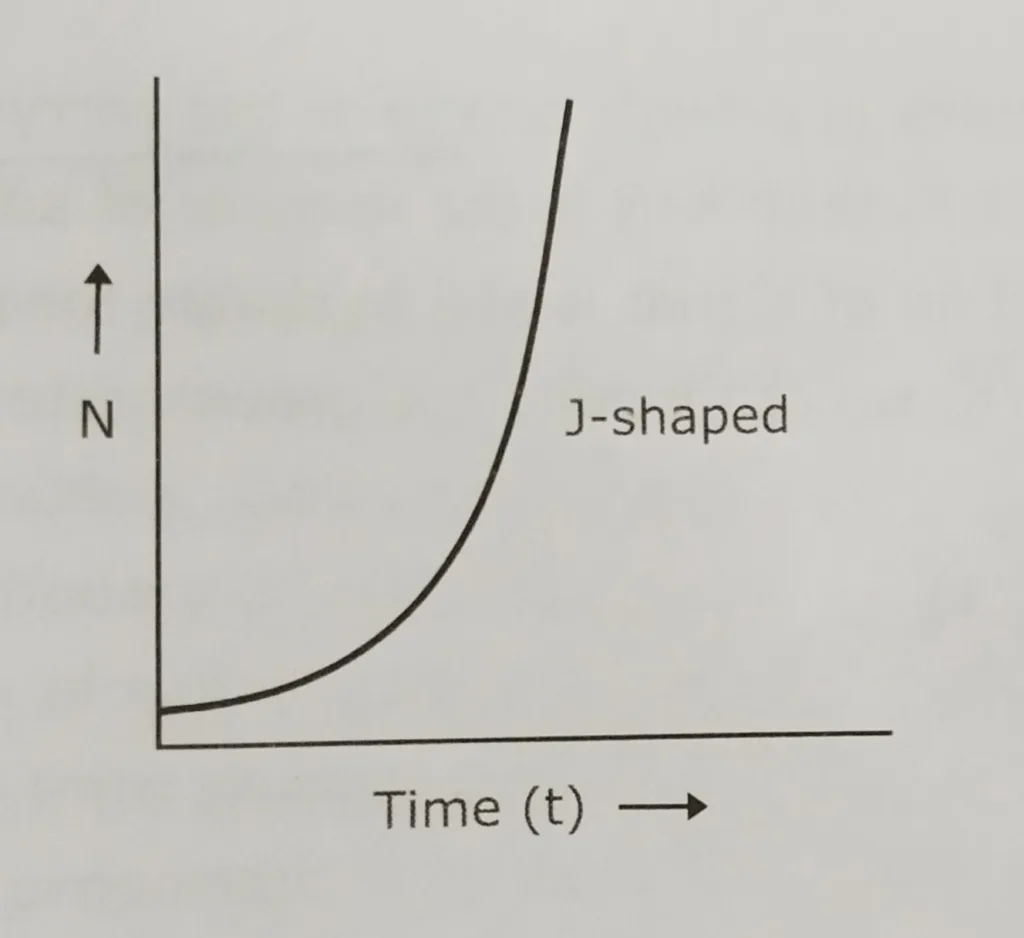
When resources (food and space) in a habitat are unlimited, all members of a species have the ability to grow exponentially. The population size that increases exponentially at a constant rate, results in a J-shaped curve when population size (N) is plotted over time (t).
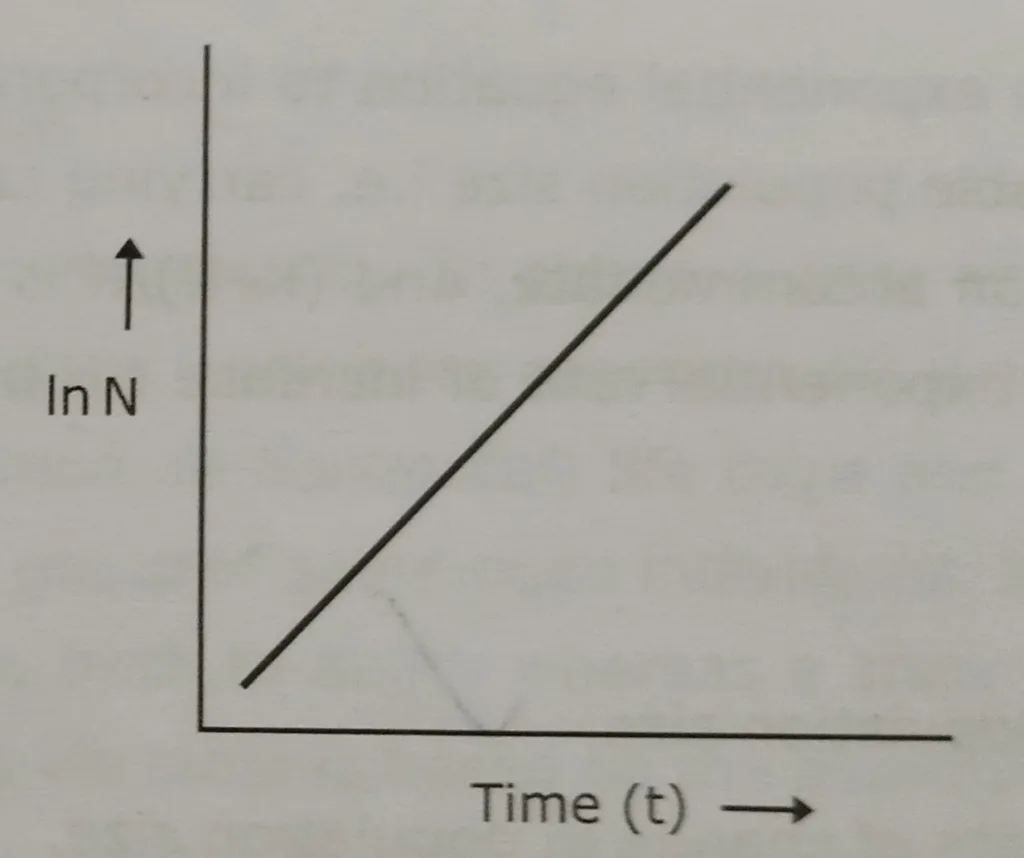
For a variety of organisms, the per capita rate of increase, r is affected by 1) the size of the organism 2) generation time.
r decreases as generation time increases.
In optimal conditions for the population, r is at its maximum rate and is called the intrinsic rate of increase (r max).
Thus, the rate of population growth under optimal conditions is dN/dt = rmax N.
rmax has been found to decrease with body weight
Exponential growth occurs when the per capita rate of increase remains above zero
Clearly, much depends on the value of the per capita rate of increase rate, r.
When r<0, the population decreases, when r= 0, the population remains constant; and when r> 0, the population increases.
When r=0, the population is again referred to as being at equilibrium, where no changes in population size will occur and there is zero population growth.
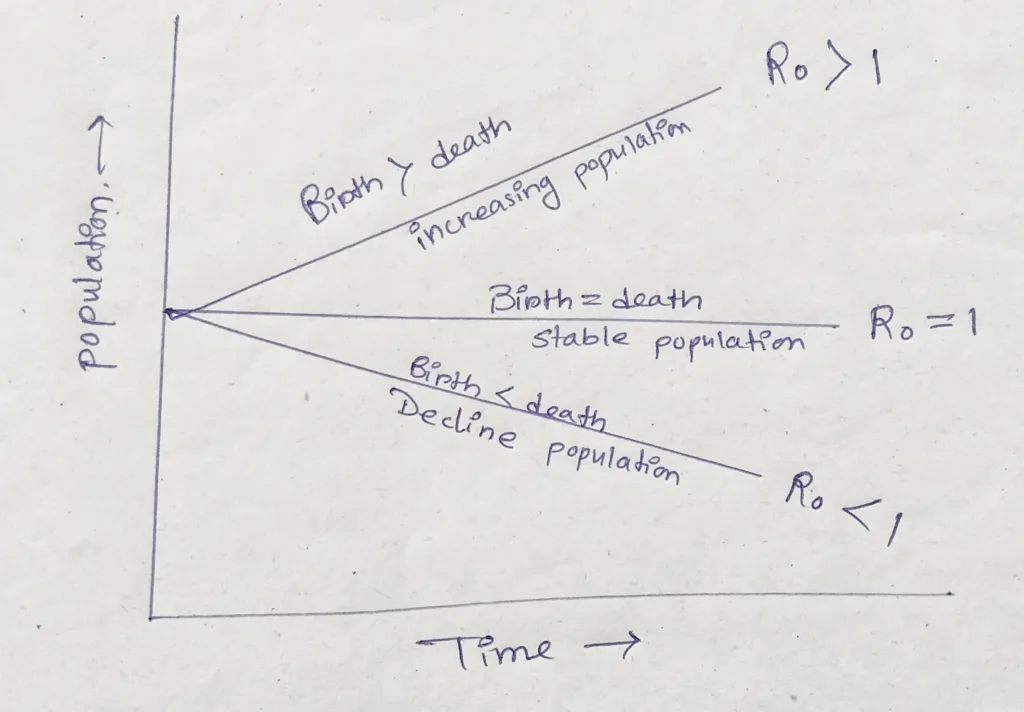
Even if r is only fractionally above 0, population increase is rapid, and when plotted graphically a J shaped curve results.
Other related notes:
- Population growth- Geometric growth: https://thebiologyislove.com/population-growth-geometric-growth/
- Doubling time:
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/MWP6iw1ccsWKGb1M/?mibextid=oFDknk
Instagram link: https://www.instagram.com/p/C7d21DmRvNA/?igsh=NnUxMzN5aDh1cWl5
