Table of Contents
Phototropin, a flavoprotein, acts as a blue light photoreceptor, which are localized in the nucleus. Phototropins are membrane associated proteins lacking a membrane spanning domain.
Structure of Phototropin:
- The N-terminal half of this molecule binds flavin mononucleotide (FMN), and carboxyl-terminal domain has characteristics of a serine threonine kinase.
- The photosensory domain, located at the N-terminus, has two LOV domains-LOV1 and LOV 2, each binding to a chromophore FMN.
- LOV domains exhibit protein sequence homology to motifs found in a diverse range of eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins involved in sensing Light, Oxygen and Voltage, hence the acronym LOV.
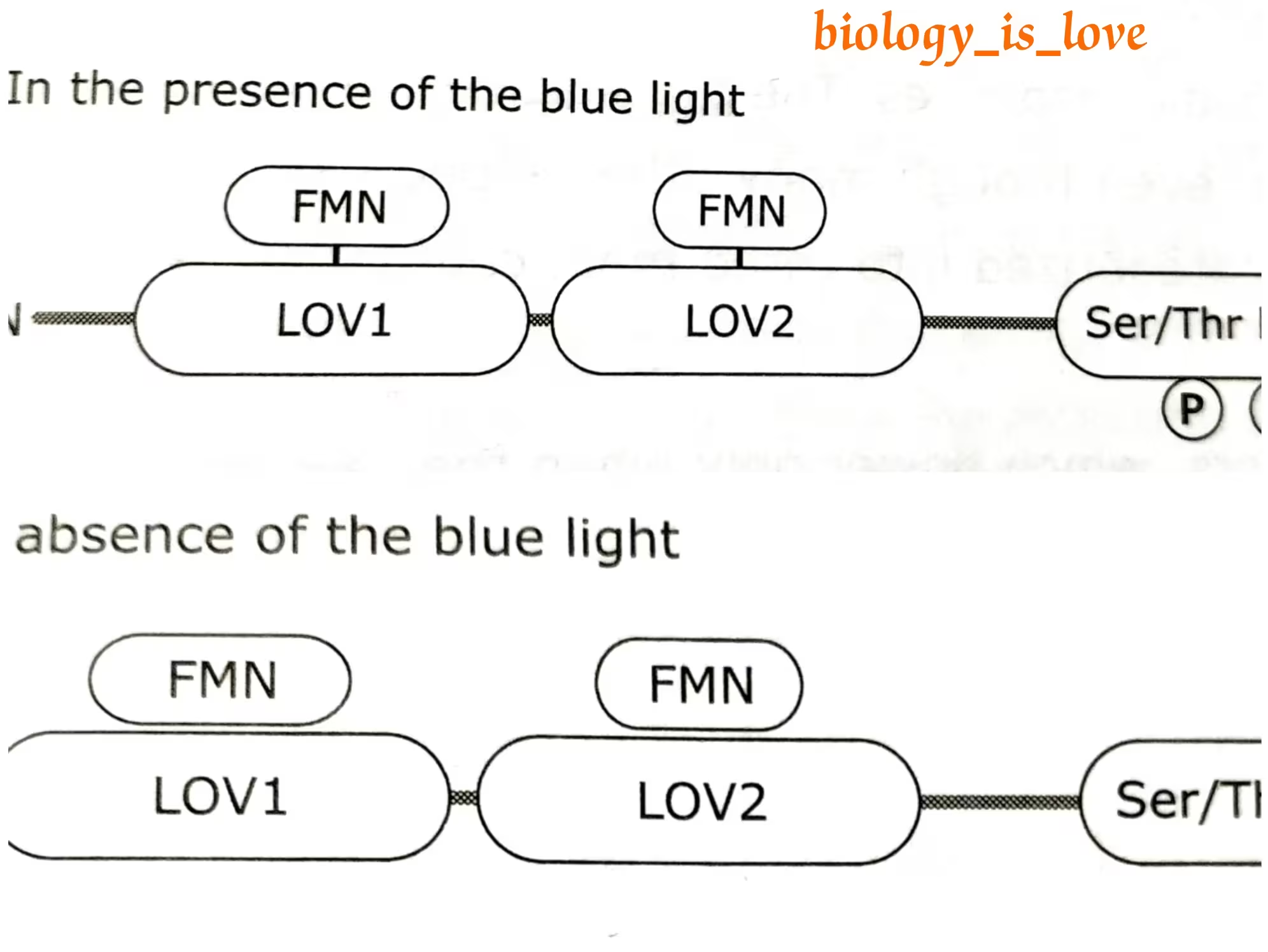
Activity in the presence and the absence of light:
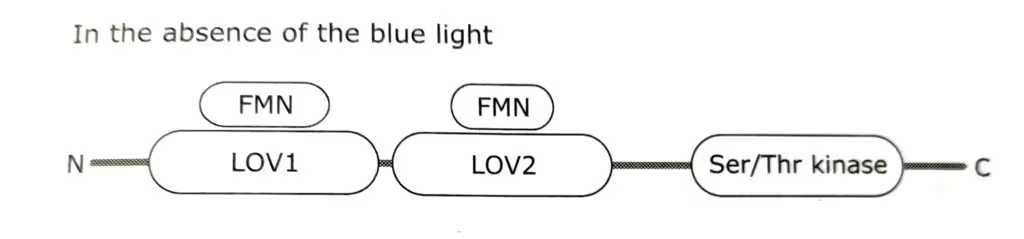
In the dark, FMN molecules are non-covalently bound to LOV domains.
Upon blue light (around 450nm) illumination, the FMN molecules become covalently bound to cysteine residues in the polypeptide.
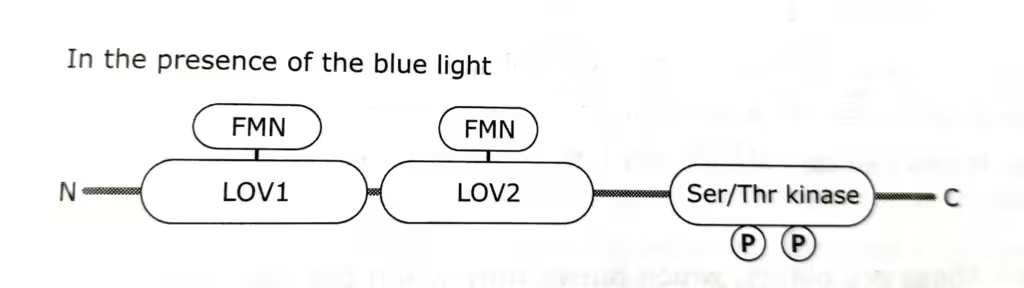
Photoexcitation of of LOV domains leads to the activation of the C-terminal kinase domain, which causes the autophosphorylation on multiple serine residues.
The major role: [Chloroplast movement]
The phototropin has a major role in regulation of phototropism and chloroplast movements.
Chloroplast movement in leaves is an adaptive feature that occurs in order to control light absorption and prevent photodamage.
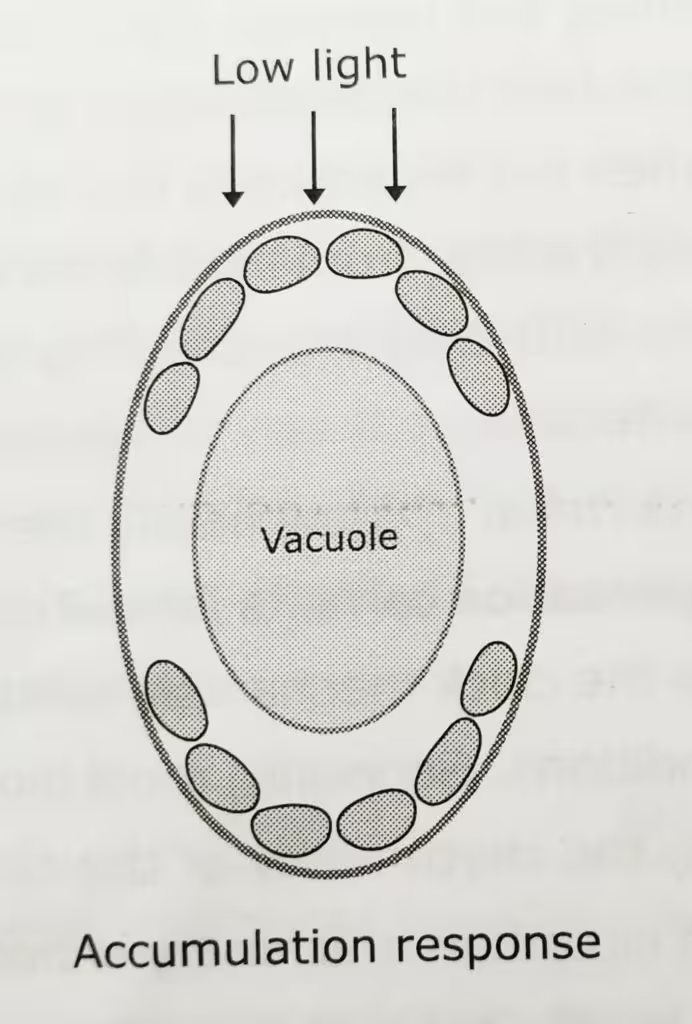
- When incident radiation is weak, chloroplasts move at the upper and lower surfaces of the mesophyll cells (accumulation response), thus maximizing light absorption.
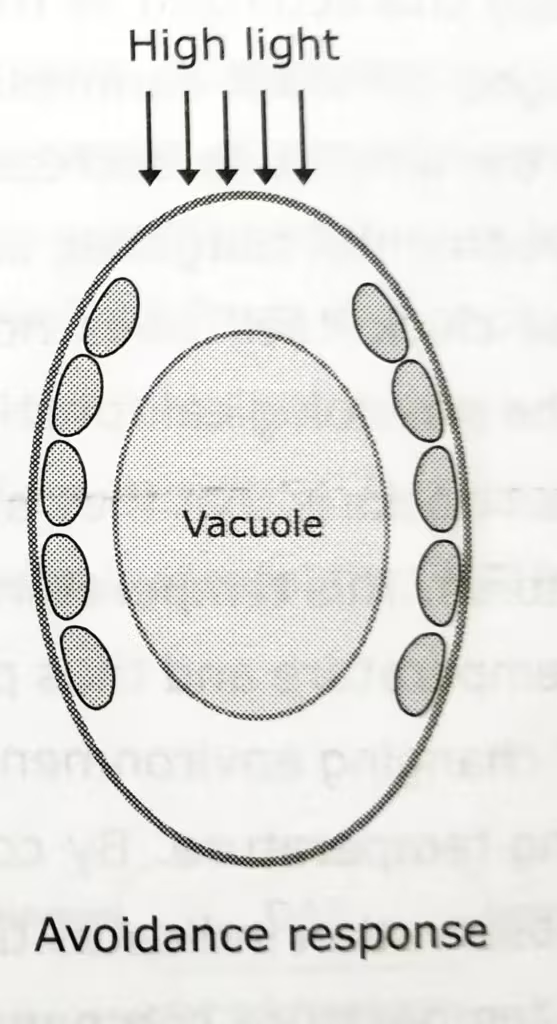
- Under high light intensity, the chloroplasts move to the cell surfaces that are parallel to the incident light (avoidance response), this minimizing light absorption.
The schematic representation to elaborate the accumulation and avoidance response:
Involvement of CHUP1 (Chloroplast Unusual Positioning1) :
Both PHOT1 and PHOT 2 mediate the accumulation response and are localized at the plasma membrane. PHOT 2 is also localized in the chloroplast envelope and probably mediates the avoidance response.
These proteins work in association with CHUP1 (Chloroplast Unusual Positioning 1) protein. Chloroplast outer envelope protein CHUP1 is essential for the chloroplast anchorage to the plasma membrane and chloroplast movement.
Other related notes:
- Photorespiration: https://thebiologyislove.com/photorespiration-or-c2-pathway/
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/Phtxa4hSNGtynXW4/?mibextid=oFDknk
Instagram link: https://www.instagram.com/reel/C8iELocy_Hr/?igsh=MTA0MDl5MDZ1OXhncQ==