Table of Contents
DBT-JRF is a biotechnology-based national-level examination. The numerical problems are very important to crack this exam. There are two parts to the exams. Part A is related mathematics and have to attempt 50 compulsory questions in this part. 50 more questions have to attempt out of 150 given questions in the part B. The question pattern and the syllabus are presented below. The numerical should be related to biochemistry, biophysics and other life science related topics. The formulas for the numerical are provided here based on the previous year questions.
Click to download the syllabus: https://rcb.res.in/upload/DBT-JRF%20BET-%202021%20Syllabus.pdf
The formulas of numerical related to Biochemistry:
- Gram equivalent= (molecular weight) / (acidity or basicity or valency or charge)
- Mole number= (weight)/ (molecular weight)
- Molarity = mole / volume (L) of solution
- Molarity = (Density / Molar mass) X 1000
- Molality = (mole of solute) / (weight of solvent)
- Normality = molarity / (acidity or basicity or valency or charge)
- Normality= (weight / gram equivalent)/ Volume (L)
- pH = -log [H+]
- [H+] = 10-pH
- pOH = -log [OH–]
- [OH–] = 10-pOH
- pH = pKa + log (salt/acid)
- pH = pKa + log (salt/base)
- pH – pKa = log (salt/acid)
- 10pH – pKa = salt/acid
- pH = pKa – log10 (acid/ base)
- 10pKa – pH = acid/ base
- Tm = 4( G+C) + 2(A+T) [Tm= the melting point of DNA]
- Specific Activity of an enzyme= (Total enzymatic activity) / (Total protein)
- Purification fold= (Specific Activity of method)/ (Specific Activity of crude extract)
- Yield = (Enzyme Activity of method / Enzyme Activity of crude extract)
- ET = Weight / Molecular weight
- Kcat = Vmax / ET
- Enzyme efficiency = Kcat / Km
- Enzyme kinetics: V= (Vmax* [S]) / (Km+ [S])
- Molecular weight of circular protein = n (molecular weight an amino acid – 18)
- Molecular weight of linear protein = n (molecular weight an amino acid – 18) + 18
- The formulas regarding chemical kinetics are in this link: https://ch301.cm.utexas.edu/help/ch302/kinetics.pdf
The formulas of numerical related to Thermodynamics:
- Kinetics: ΔG = ΔG° + RTlnK
- ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
- Transport: ΔG = RTlnK + Z.F.Ψ
- Electrode potential: ΔG = – nFE cell
- Osmosis: ΔG = RTln Cf / Ci
- If a drop of sweat evaporates from body, the work dome , W = P (V2 – V1)
The formulas of numerical related to Bioreactor:
- In a pipe, Reynold’s number (Rei) = (stirrer speed (V) X diameter (D) X density (ρ)) / Viscosity (µ)
- In a turbine impeller, Reynold’s number (Rei) = (stirrer speed (N) X diameter2 (D2) X density (ρ)) / Viscosity (µ)
- {Power absorption (P) / V } α N3D2
- If, Rei > 5 X 103 then, Mixing time (Nitm) is constant.
- then, Nitm= (1.54 X volume of tank) / diameter3
- Volumetric concentration factor = (Volume of feed) / (Volume of retentate)
- Dilution rate (D) = flow rate (f) / volume of the reactor (v)
- VVM (aeration rate) = velocity (L/min) / volume (L)
- Volume of the fermenter (l) = Amount of product (kg/d) / volume productivity (g/L/h)
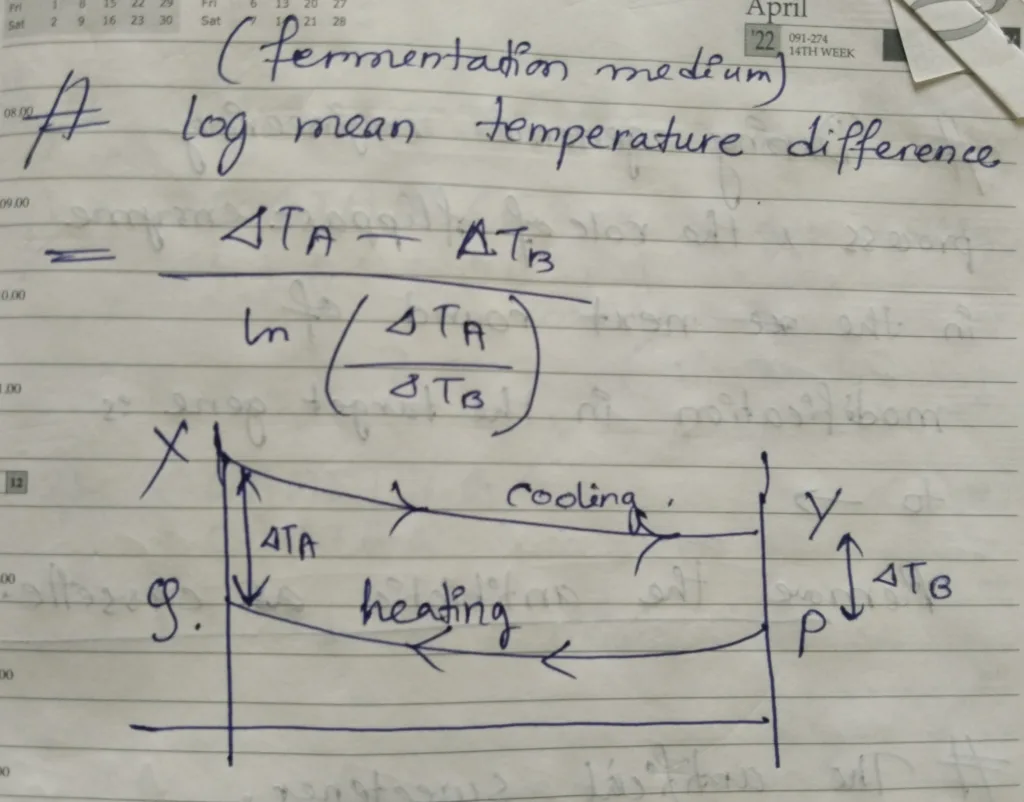
- In fermentation medium, log mean temperature difference = {(ΔTA– ΔTB)} / {ln (ΔTA/ ΔTB)} [The explanation is in the picture below]
The formulas of numerical related to Biophysics:
- Angular velocity (ω) = 2πN / 60 (rad/sec)
- The rate of heat transferred = Q/t= {k X A X (T2 – T1)} / d
The formulas of numerical related to Microbiology:
- Doubling time or generation time = 0.693 / specific growth rate
- Generation time = (log Nt – log No) / log 2
- CFU (Colony forming unit / ml) = ( no. of colonies X Dilution factor) / Volume of culture
- Monod Growth kinestics: µ= (µmax [S]) / (ks + [S])
[Except these, the formulas of mensuration and trigonometry should be prepared to solve the problems of Part A of DBT-JRF.]
Another content useful for CSIR NET & DBT aspirants:
- Nodulation in leguminous plants: https://thebiologyislove.com/the-formation-of-nodule-by-rhizobium-species/
- MHC molecules: https://thebiologyislove.com/major-histocompatibility-complex-immunology/

