Table of Contents
In noncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to the enzyme other than the active site. The three-dimensional configuration is changed due to the binding of the inhibitor and it leads to the inhibition of the reaction. There are two type of noncompetitive inhibition. These are pure and mixed. Here, the pure non-competitive (non-competitive inhibition) is discussed.
Mechanism:
In pure non-competitive inhibition, substrate, and inhibitor bind at different sites on enzyme and binding of inhibitor does not affect binding of substrate. The inhibitor binds to either free enzyme or the ES complex. Hence, inhibition is not reversed by increasing the concentration of substrate.

Vmax and Km, in non-competitive inhibition:
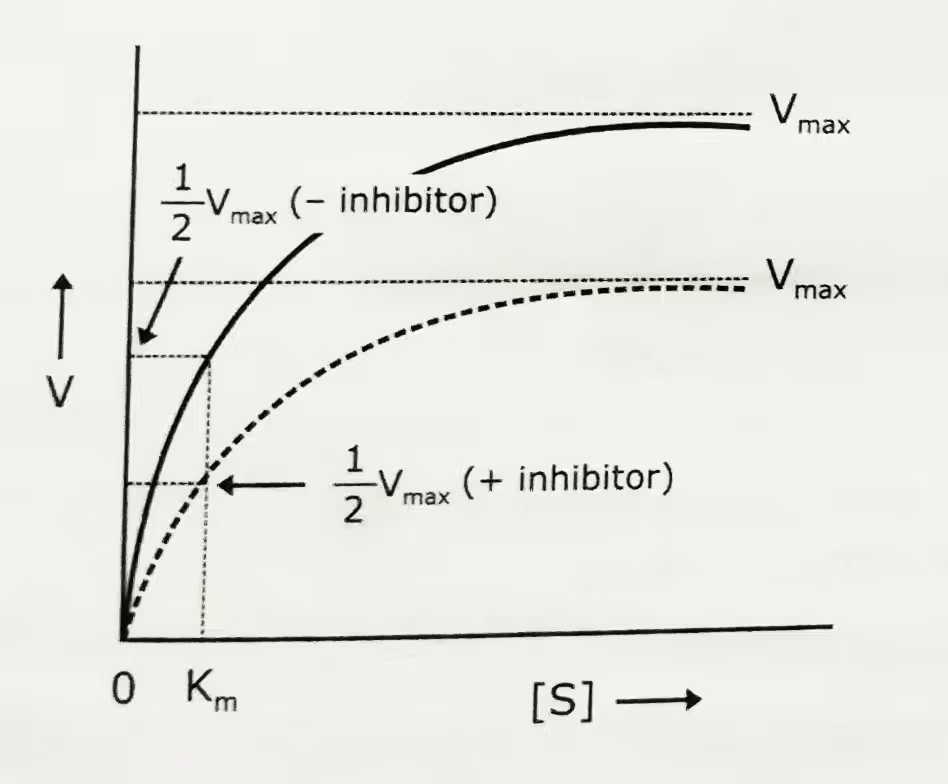
Pure non-competitive inhibition occurs if KI = KI’. In this type of inhibition, Vmax decreases and Km stays constant.
The Michaelis-Menten equation of Noncompetitive inhibition:
In the presence of pure non-competitive inhibitor, the Michaelis-Menten equation becomes,
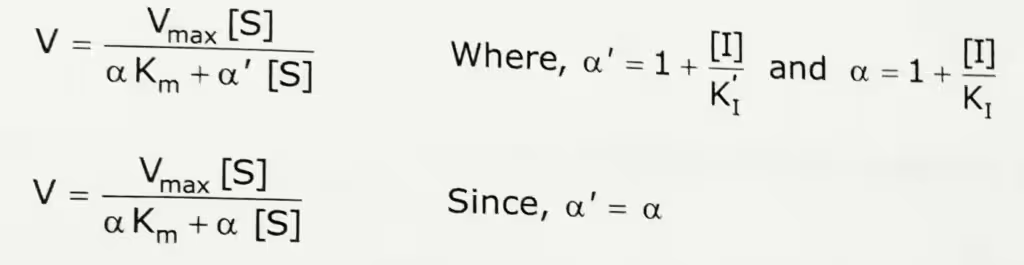
The double-reciprocal form of the above equation:
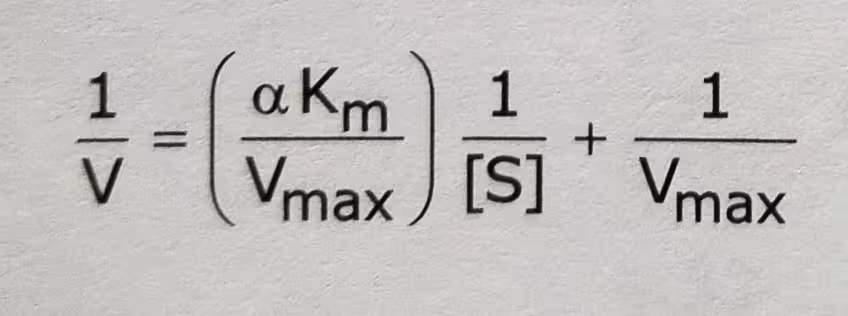
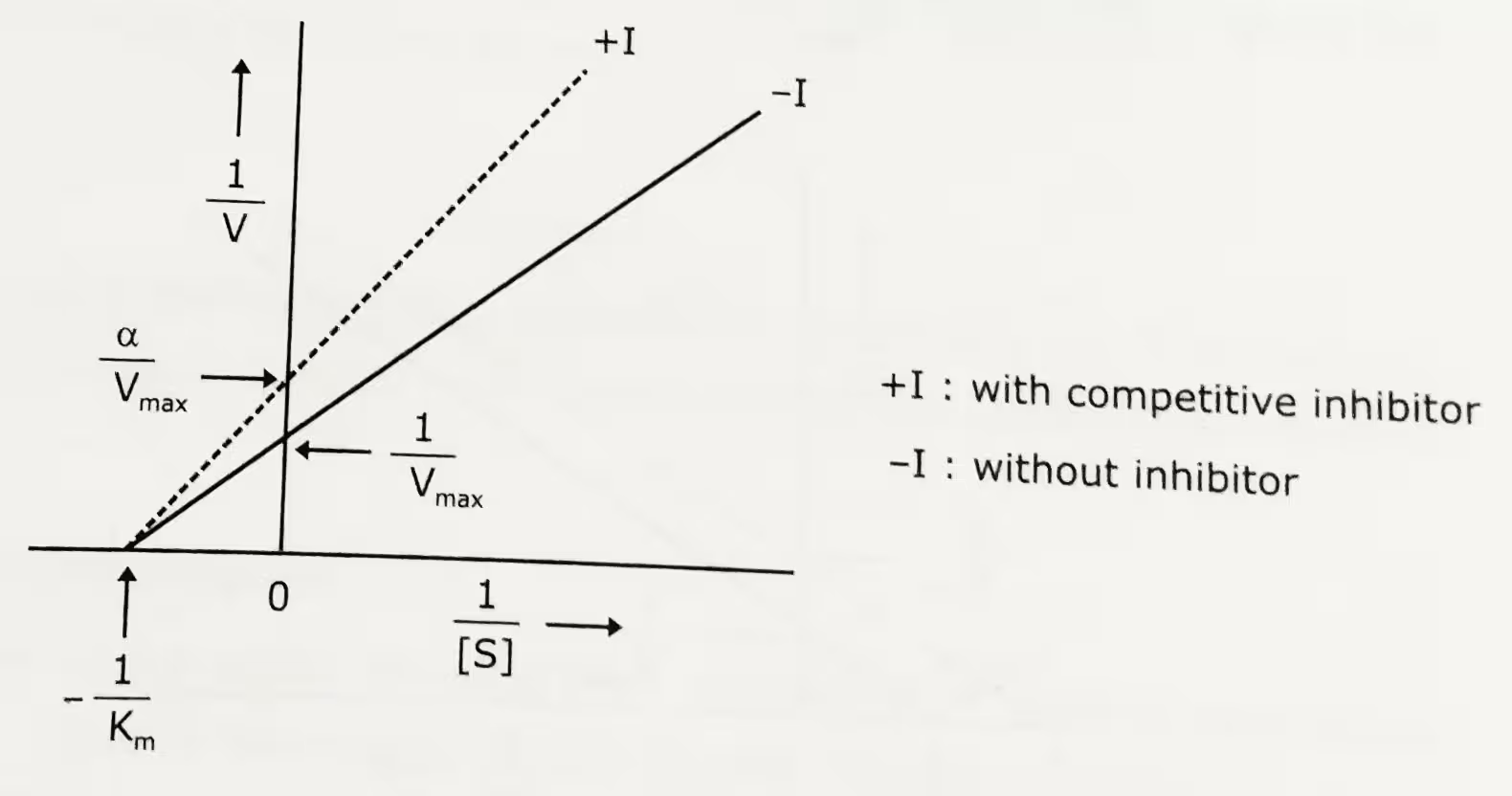
Michaelis-Menten plot: Uninhibited enzyme activity vs pure non-competitive inhibition:
Lineweaver-Burk plot: Uninhibited enzyme activity vs pure non-competitive inhibition:
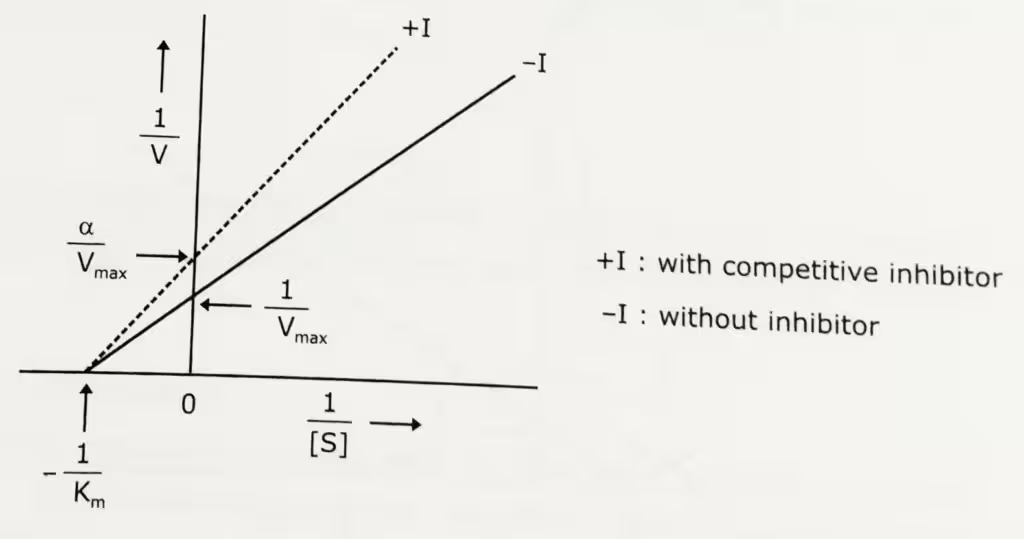
Other related notes:
Competitive inhibition: https://thebiologyislove.com/competitive-inhibition-graph/
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/XUsfYtegfzHByCio/?mibextid=oFDknk
Instagram link: https://www.instagram.com/p/C8KQdGnSFKc/?igsh=MTBqYWE3aWlpdHE5NQ==