Table of Contents
MHC or Major Histocompatibility Complex is a group of genes, present on the cell surface and carries a major role in immune response. This gene is present in chromosome 6. This MHC is three types- MHC I, MHC II, MHC III.
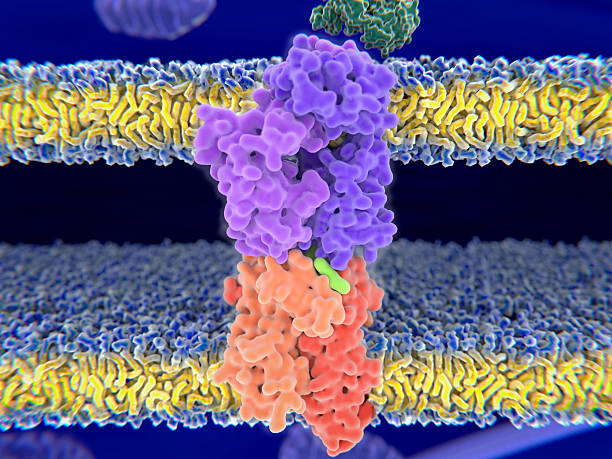
Structure of MHC I (Major Histocompatibility complex I)
MHC I is activated by intracellular protein (viral protein). MHC I, is present in all nucleated cells except sperm cell, play a crucial role in immune response.
This complex consists of the alpha (α) chain, which is heavy (chromosome 6) and beta (β) chain, which is light (chromosome 15). Alpha chain is made up of three subunits- α1, α2 (carbohydrate domain), α3 and beta is only one microglobulin β2. There is a non covalent interaction between α3 and β2. .
The structure of MHC I is as follows:-
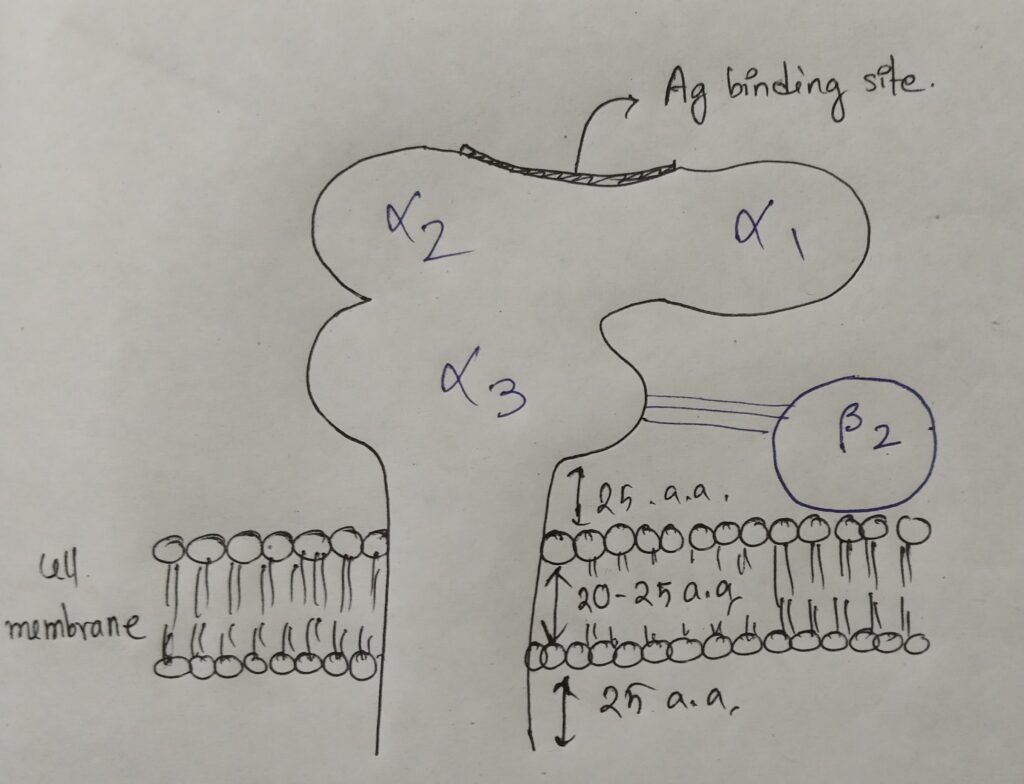
The comparative study of α and β chains of MHC I :
| Features | α chain | β chain |
| 1) Variable | α1, α2 | none |
| 2) Constant | α3 <– CD8 (binds to TH cell) | β2 |
| 3) Nature | Integral | Peripheral |
| 4) Most conserved | α3 | none |
| 5) Molecular weight (KD) | 45 | 12 |
| 6) Number of Amino acids | 340-350 | 100 |
| 7) CD 8 binding site | α3 | none |
| 8) Chromosome number | 6 | 15 |
| 9) Glycosylation | α2 | none |
| 10) Protein binding site | α1, α2 | none |
| 11) Type of chain | Heavy | Light |
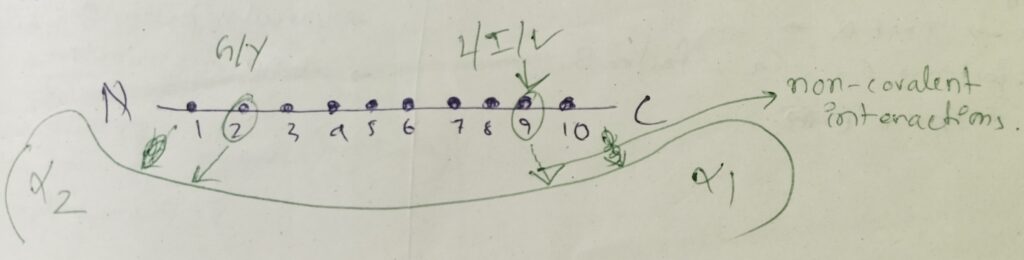
Peptides that binds to MHC I:
The peptide should be 8-10 amino acids long. The concept will be more understandable by the picture below:
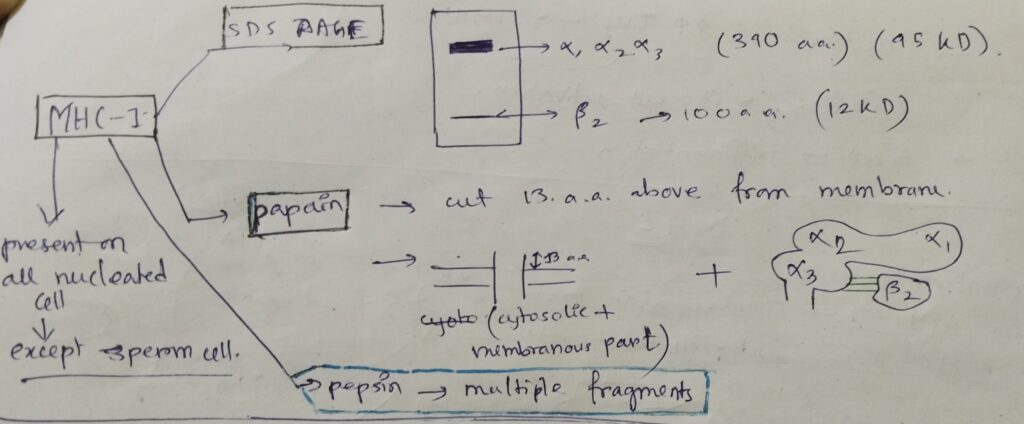
Treatment of MHC I by the followings:
- In SDS- PAGE, two bands are obtained. One is a thick band, consists of all the α subunits. Another one is thin of β2.
- After digestion by papain, two parts, which is shown in the picture below. Papain always cut 13 amino acids above from the cell membrane.
- After digestion by pepsin, multiple fragments are obtained.
Structure of MHC II (Major Histocompatibility complex II)
MHC II is activated by extracellular protein (bacterial protein). MHC II, is mainly present on APC (Antigen presenting cells). It always lacks in nerve cell, play a crucial role in immune response.
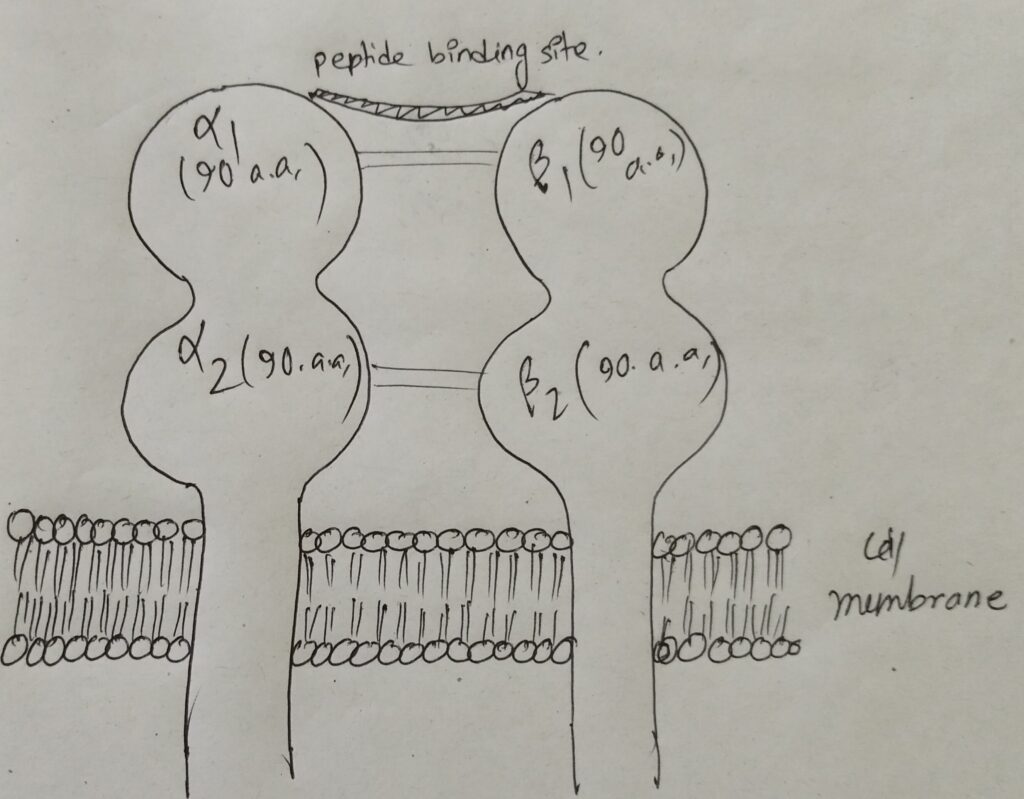
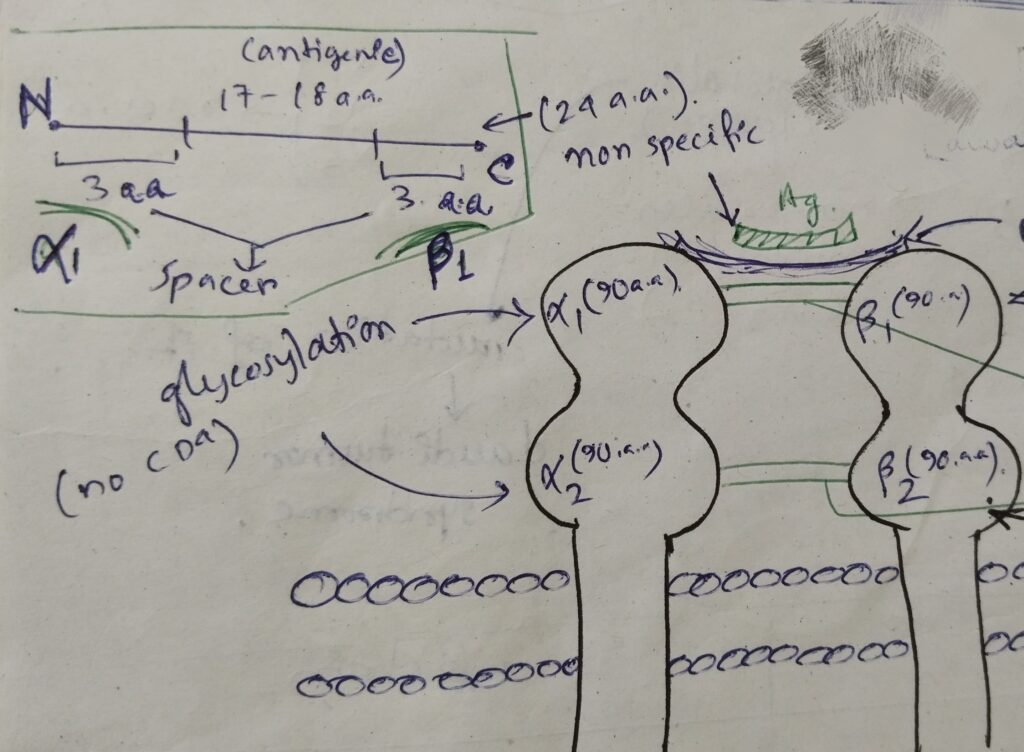
This complex consists of the alpha (α) chain (chromosome 6) and beta (β) chain (chromosome 6). Alpha chain is made up of two subunits- α1, α2 and beta is made up of two subunits- β1, β2. There are two non covalent interactions between α and β.
The structure of MHC II is as follows:-
The comparative study of α and β chains of MHC I :
| Features | α chain | β chain |
| 1) Domain | α1, α2 | β1, β2 |
| 2) Glycosylation | both | β1 |
| 3) Variable domain | α1 | β1 |
| 4) Constant domain | α2 | β2 |
| 5) Chromosome | 6 | 6 |
| 6) Polymorphism | α1 | β1 |
| 7) CD4 | none | β2 |
| 8) Peptide binding | α1 | β1 |
Peptides that binds to MHC I:
The peptide should be 24 amino acids long. The concept will be more understandable by the picture below:
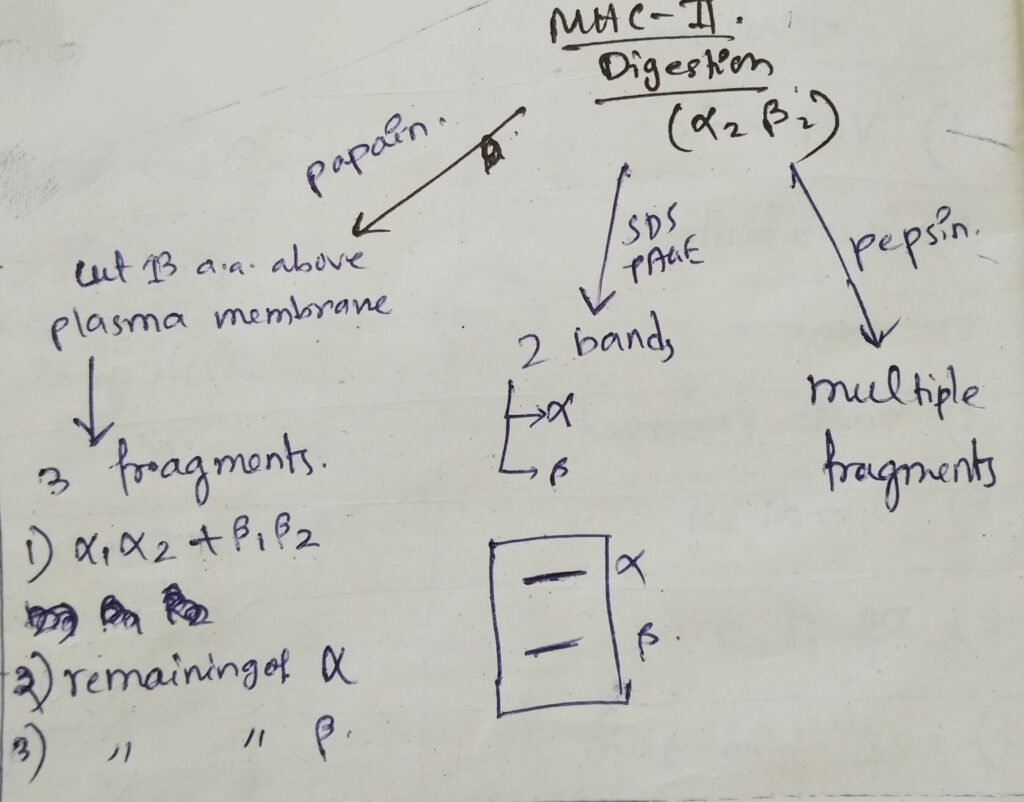
Treatment of MHC II by the followings:
- In SDS- PAGE, two bands are obtained. Both are similar bands.
- After digestion by papain, three parts, which is shown in the picture below. Papain always cut 13 amino acids above from the cell membrane.
- After digestion by pepsin, multiple fragments are obtained.
[HLA-DR determinants code for class II MHC. ]
Structure of MHC III (Major Histocompatibility Complex III)
The features are as follows:
- It is a secretory protein.
- It has no role in antigen presentation.
- It has no structural similarities with MHC I and MHC II.
- It plays a crucial role in immune response.
- it provides cytokines (TNFα), complement factor (C2, C4 and factor B), hydrolytic enzymes and HSP (Heat shock proteins).
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/CemVZSvSXtBVJkgP/?mibextid=Nif5oz
YouTube Link:
Instagram Link:
Visit our website for more CSIR NET topics: https://thebiologyislove.com/category/csir-net/
Another content useful for NEET, CSIR NET & DBT aspirants:
- Nodules formation in plants: https://thebiologyislove.com/the-formation-of-nodule-by-rhizobium-species/
- Numerical for DBT-JRF Exam & CSIR NET [2024]: https://thebiologyislove.com/numerical-for-dbt-jrf-exam-csir-net-2024/