Table of Contents
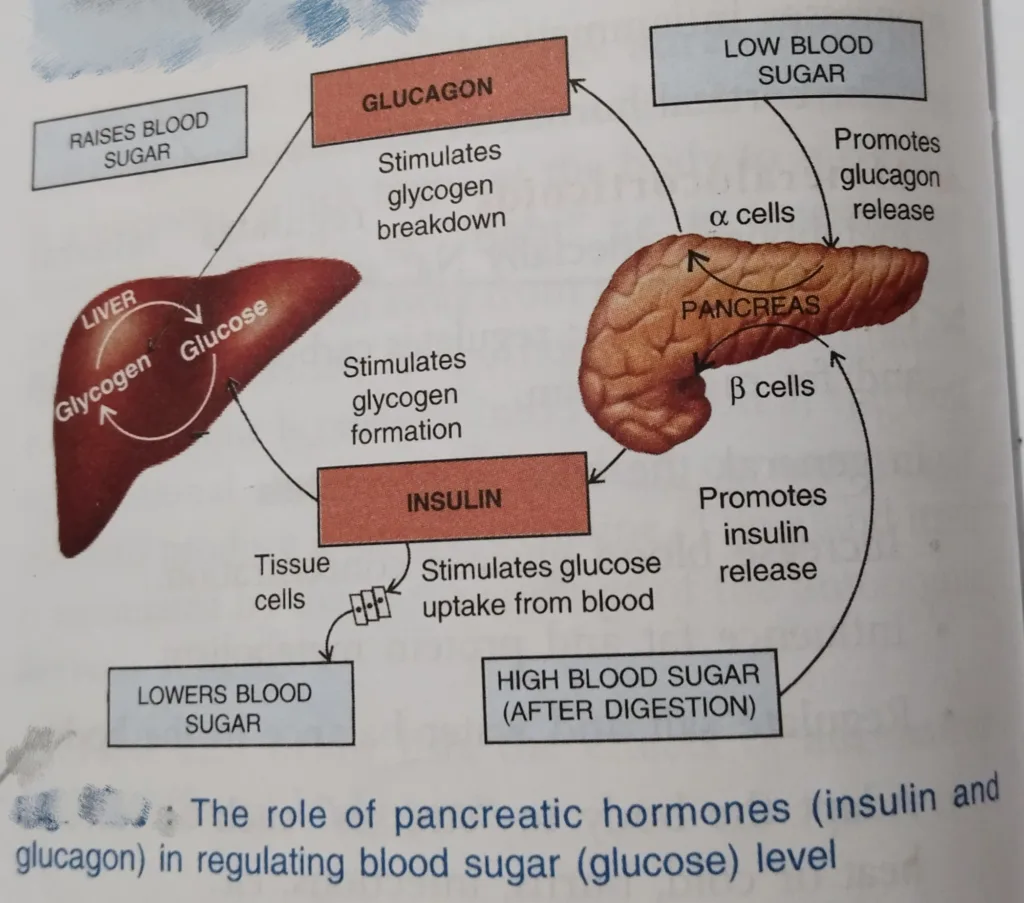
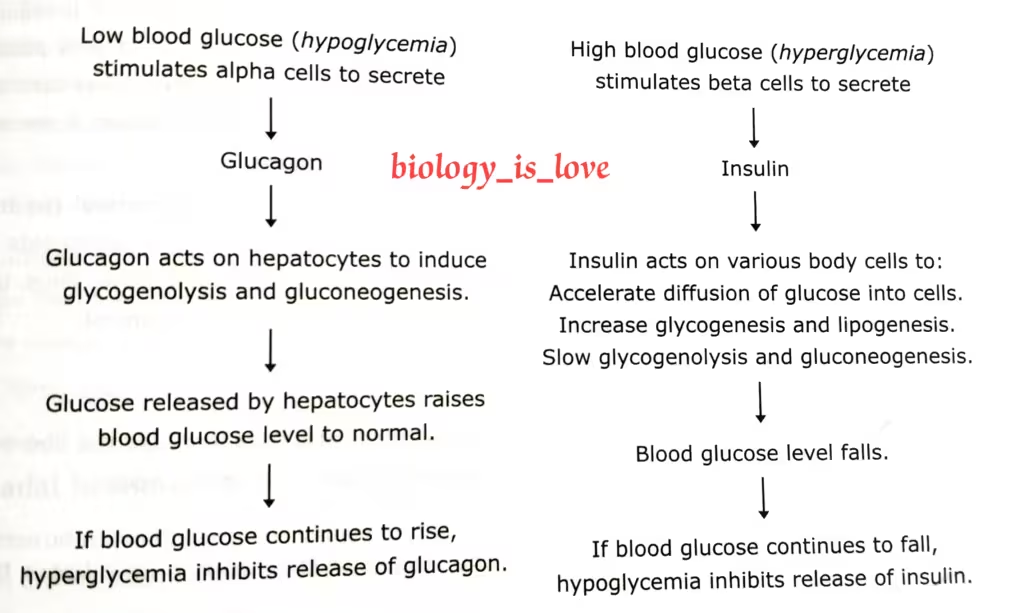
Insulin and glucagon exert opposite action on blood sugar. Glucagon increases and insulin decreases blood sugar level. This is called dual controls of hormones.
Control of secretion of Insulin and Glucagon
Control of Insulin Secretion
Insulin secretion is stimulated when blood glucose level increases above normal level. A mixture of amino acids triggers insulin secretion. Gastrointestinal hormone like gastrin, pancreozymin, cholecystokinin also stimulates insulin secretion.
Control of Glucagon Secretion
When blood sugar levels drops, glucagon secretion is stimulated. Glucagon maintains equilibrium by elevating blood sugar level. Besides this amino acids and gastrointestinal hormones also trigger glucagon secretion.
Glucagon is also called anti-insulin hormone and hyperglycemic hormone.
Schematic representations is presented below to elaborate on the dual control of insulin-glucagon:
Other related notes:
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/yDfbJhUdveEFyKUF/?mibextid=oFDknk