Table of Contents
Cytokinin signaling pathway is regulated by the Ubiquitin 26S proteolysis system. The signaling pathway is discussed in this section. It is important for any kinds of Life Science related competitive exams.
Receptor:
CRE1, AHK2, AHK3.
CRE1 (Cytokinin Response 1):
CRE1 (Cytokinin Response 1) a transmembrane protein that contain a conserved extra-cellular Cytokinin-binding domain called the CHASE domain.
AHK (Arabidopsis His Kinase)
In the Arabidopsis cytokinin signal transduction pathway, hybrid Histidine sensor kinases, AHK (Arabidopsis His Kinase) serve as cytokinin receptor.
Ligand:
Cytokinin
Signaling pathway:
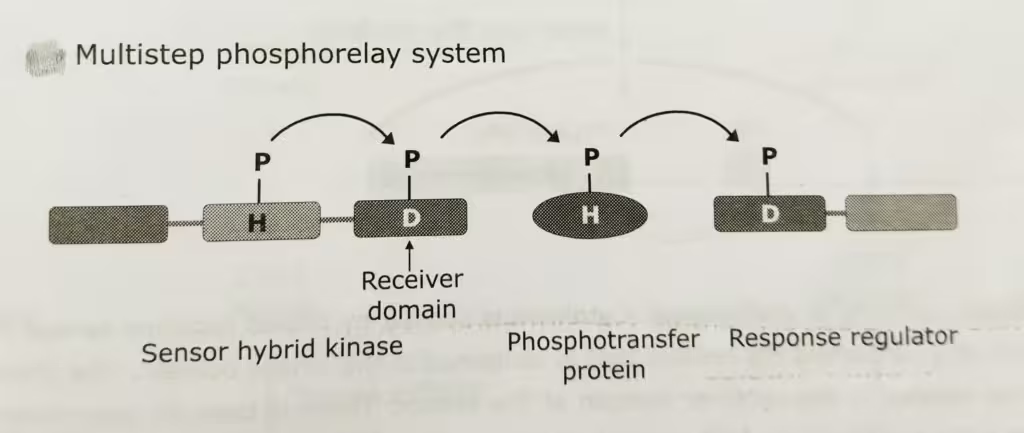
Two component Phosphorelay system
The description of Cytokinin signaling pathway
The two component signaling elements identified in the Arabidopsis from multistep phosphorelay pathways consisting of a hybrid sensor kinase that includes a sensor histidine kinase and receiver domain in one molecule, a histidine containing phosphotransfer protein and response regulator.
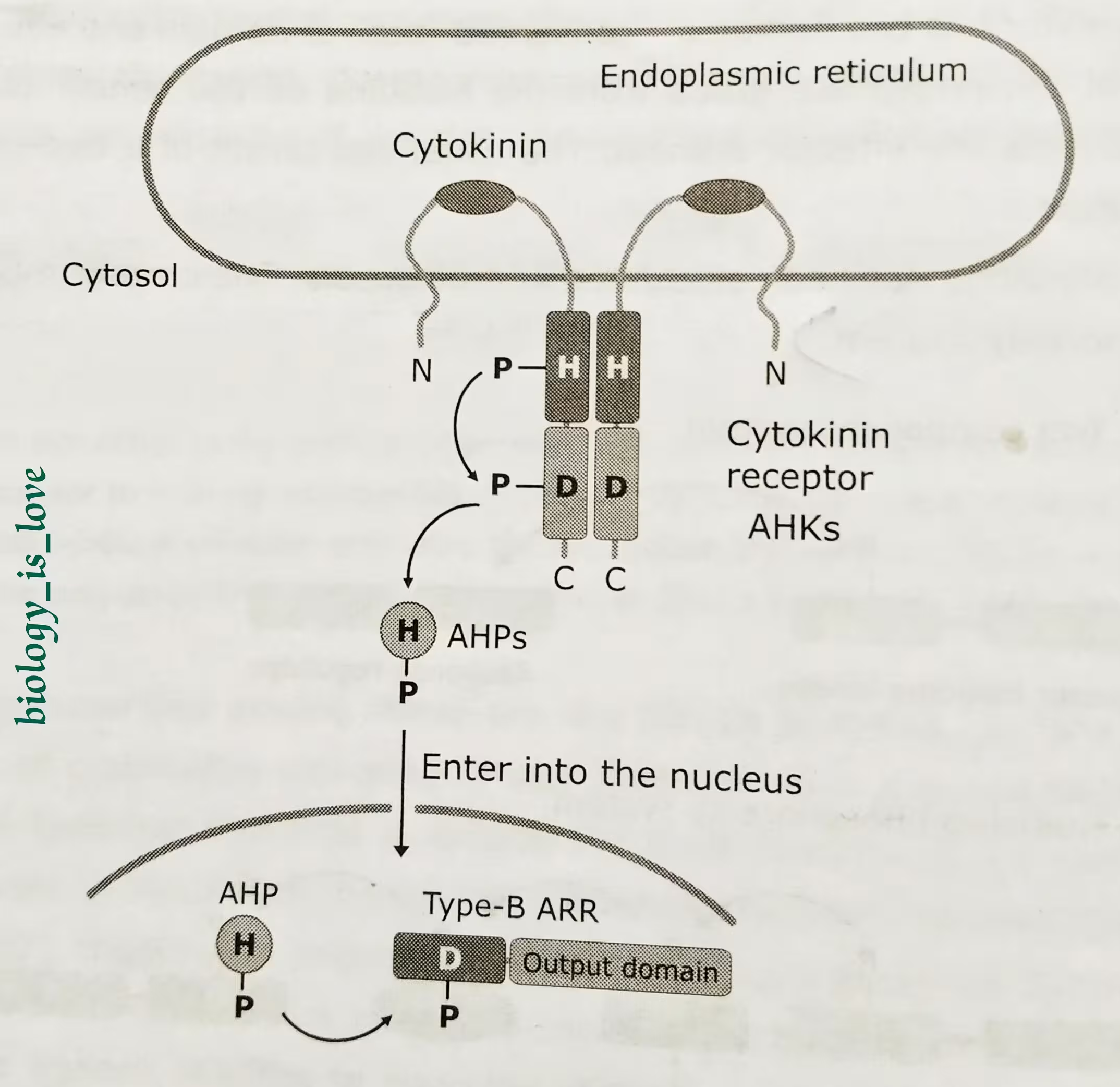
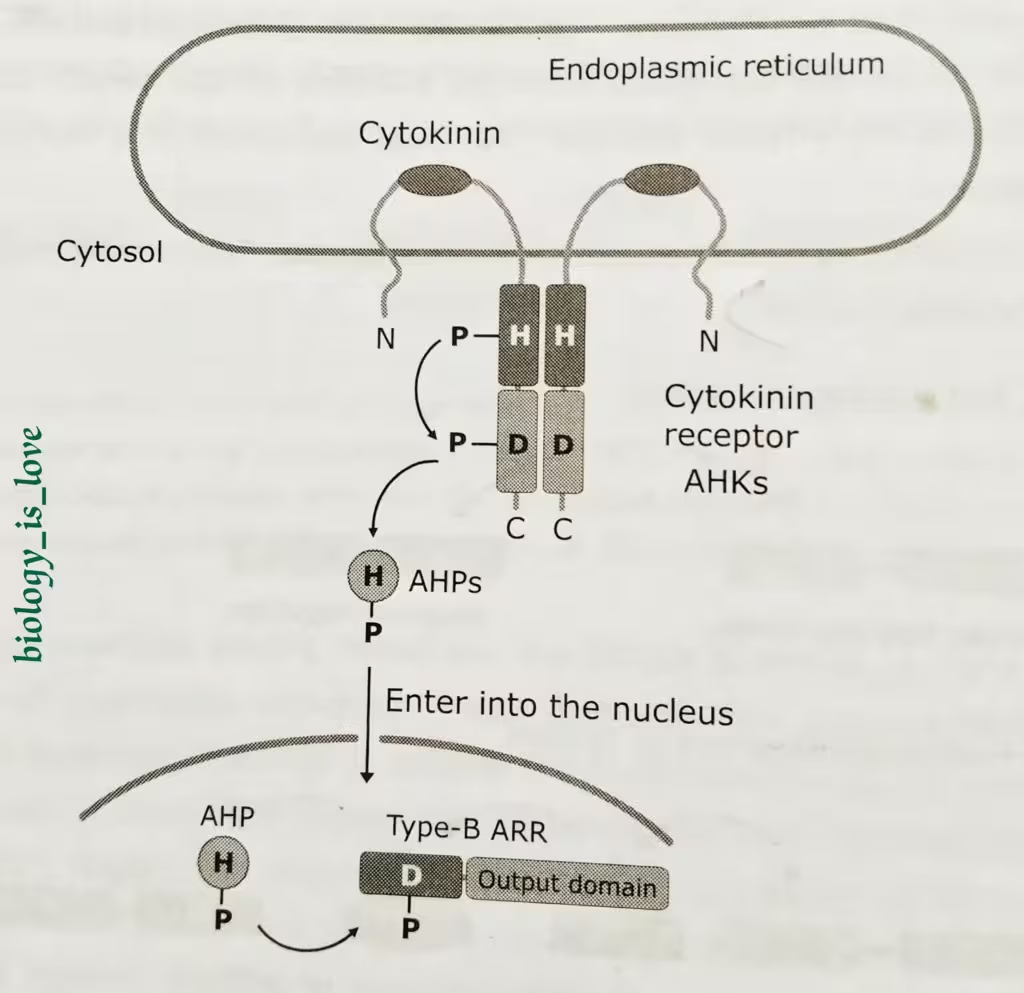
The steps of cytokinin signaling pathway:
- In the Arabidopsis cytokinin signal transduction pathway, hybrid Histidine sensor kinases, AHK (Arabidopsis His Kinase) serve as cytokinin receptor.
- Cytokinin binds to the CHASE domain of AHK. Cytokinin binding triggers autophosphorylation of AHK at histidine residue.
- The phosphorelay system begins with the transfer of the phosphoryl group first to an aspartic acid residue in the receiver domain and then to a histidine residue in a separate
- The phosphorylated AHPs migrate to the nucleus where the phosphoryl group is transferred to an aspartic acid residue in nuclear response regulators (ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATORs, ARRs) which can activate or repress transcription.
- Histidine phosphotransfer proteins act as signaling shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus in a cytokinin-dependent manner.
The schematic representation of Cytokinin signaling pathway:
ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATORs, ARRs
- There are two primary classes of ARRs in Arabidopsis names type-A and type-B ARRs.
- The Type-A ARRs are made up solely of a receiver domain and type-B ARRs consist of a receiver domain and a output domain containing DNA-binding and transcription activation domain.
- The type-B ARRs are transcription activators.
- The phosphorylation of type-B ARRs activates the output domain to induce transcription of type-A ARRs encoding genes and various cytokinin responsive genes which mediate the response of the cell to cytokinin.
- In contrast with type-B ARRs, most of the type-A ARRs are the negative regulators of cytokinin signaling thus, dampening cytokinin responses.
- The E3 ubiquitin ligase, SCF KMD negatively regulate the cytokinin response by ubiquitination of type-B ARR for proteosome degradation.
Results:
Cytokinin induce cell division, cell expansion in cotyledon, chloroplast and etioplastic development, suppression of apical dominance and senescence and differentiation of in vitro cultured cells.
Other related notes:
- Auxin biosynthesis: https://thebiologyislove.com/auxin-biosynthesis-pathway-2-types/
- Auxin signaling pathway: https://thebiologyislove.com/auxin-signaling-pathway/
- Gibberellin signaling pathway: https://thebiologyislove.com/ga1-gibberellin-signaling-pathway/
- Ethylene signaling pathway: https://thebiologyislove.com/ethylene-signaling-pathway/
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/nk46B4HxzNxqmvXv/?mibextid=oFDknk
Instagram link: