Table of Contents
The competitive inhibition graph is presented with a detailed explanation. The structure of a competitive inhibitor closely resembles that of the enzyme’s normal substrate. Because of its structure, a competitive inhibitor binds reversibly to the enzyme’s active site. The inhibitor forms an enzyme-inhibitor complex (EI) that is equivalent to the ES complex.
The Effect of the Competitive Inhibitor:
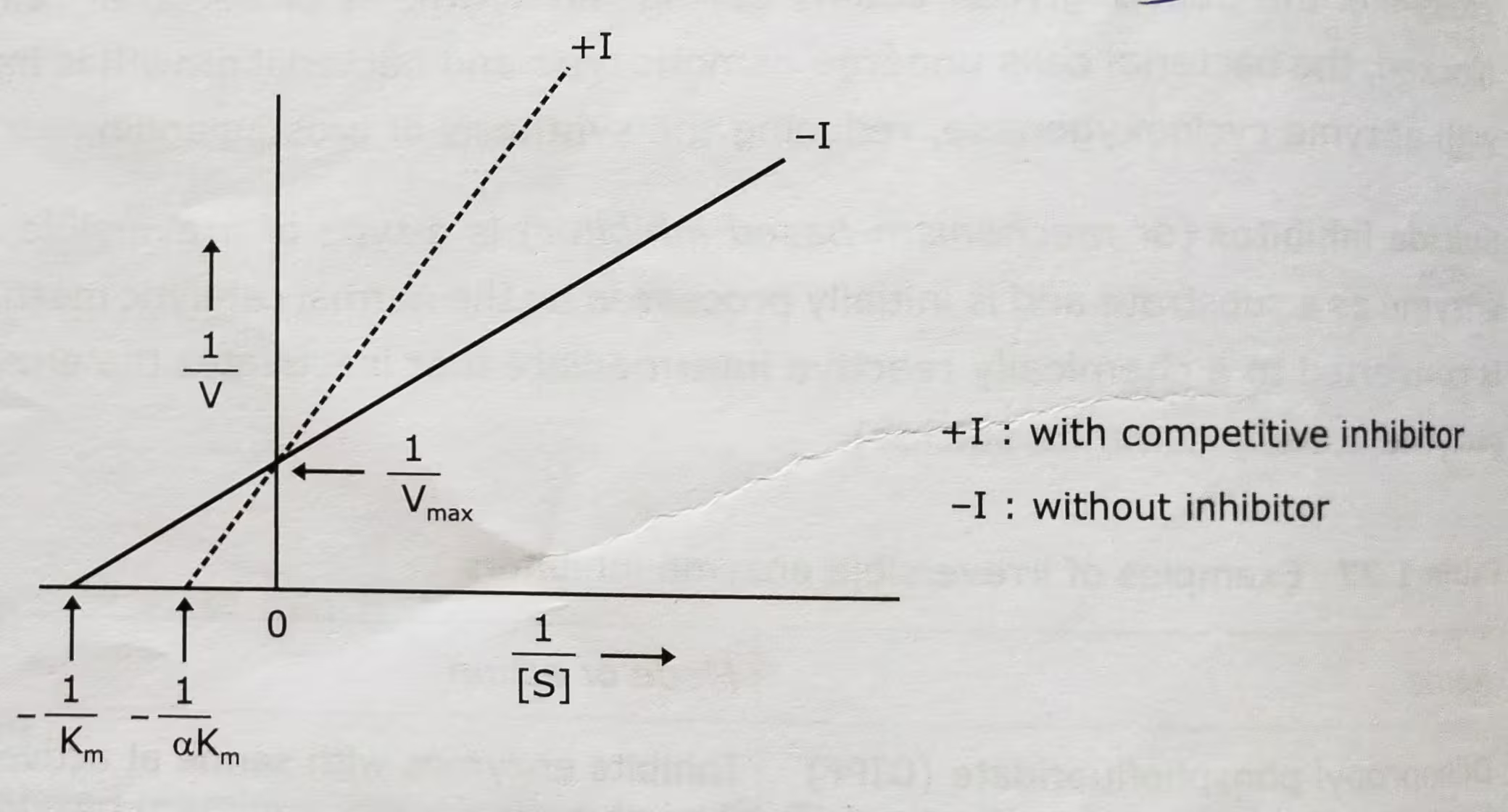
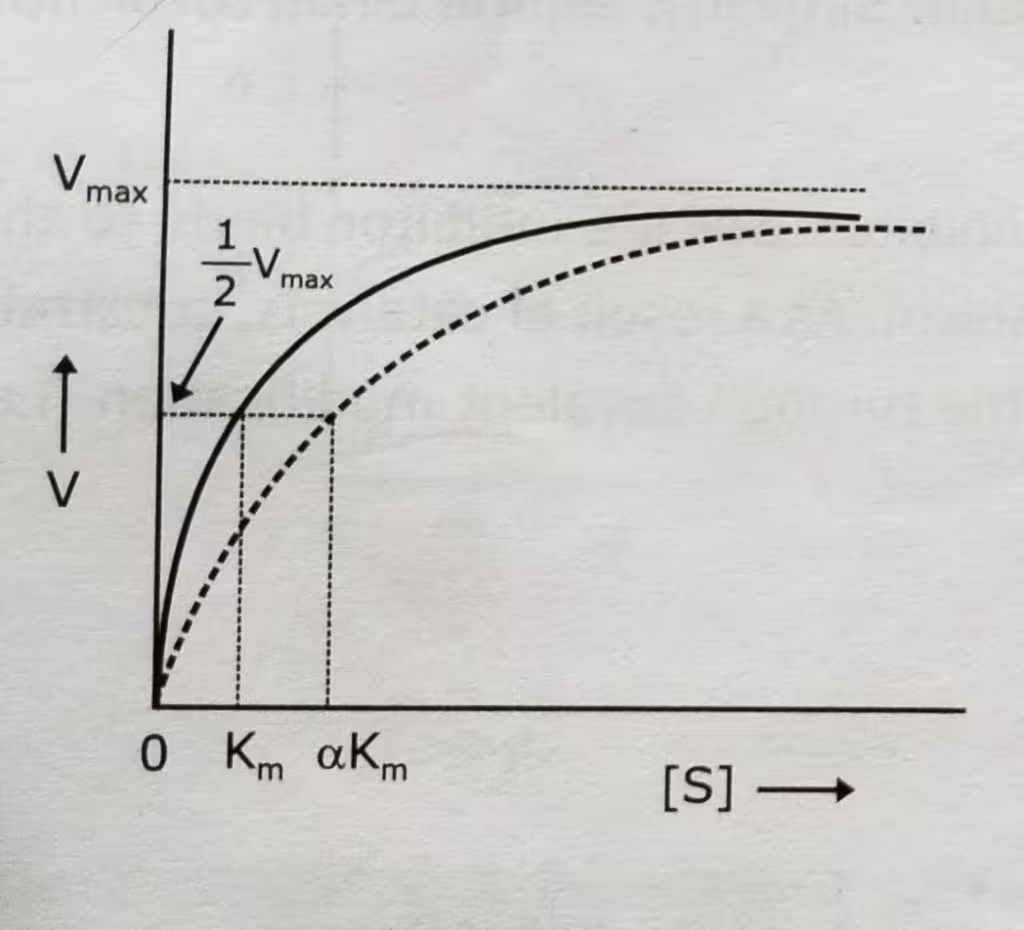
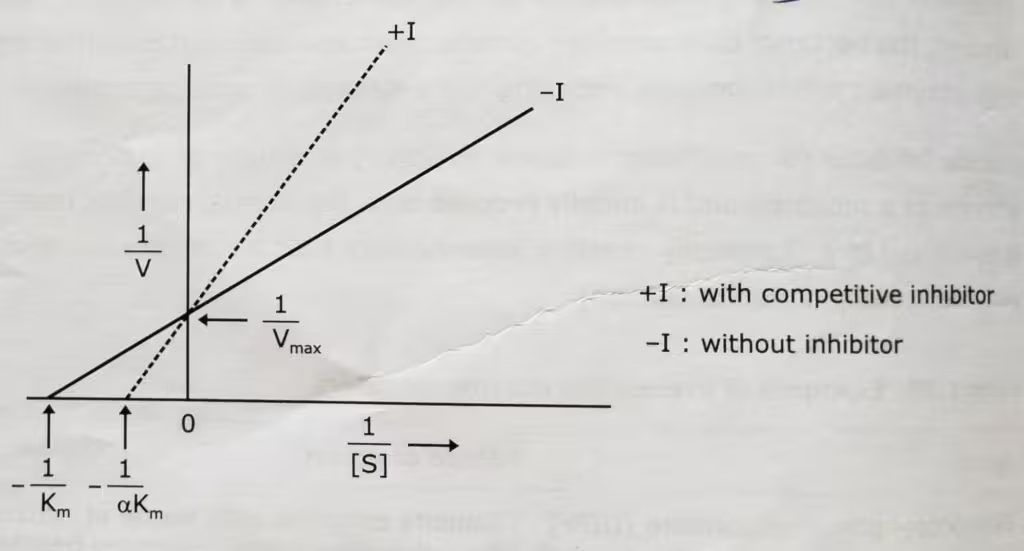
The effect of a competitive inhibitor on activity can be reversed by increasing the concentration of substrate. At high [S], all the active sites are filled with substrate, and reaction velocity reaches the value observed without an inhibitor.

Vmax and Km, in competitive inhibition:
In competitive inhibition, Vmax stays the same and Km increases. But the inhibitor does not effect the turnover number of the enzyme.
The Michaelis-Menten equation of Competitive inhibition:
In the presence of the competitive inhibitor,

Competitive Inhibition Graph- Michaelis-Menten plot: Uninhibited enzyme activity vs Competitive inhibition:
The Double-Reciprocal equation of Competitive inhibition:
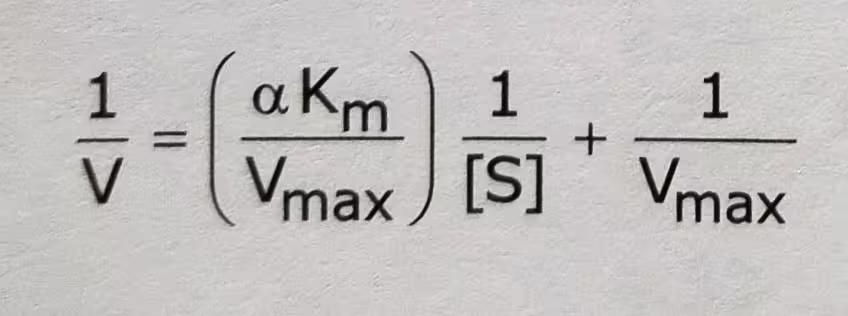
Competitive Inhibition Graph- Lineweaver-Burk plot: Uninhibited enzyme activity vs Competitive inhibition:
Examples of Competitive Inhibition:
- Clinical treatment of methanol poisoning is a classic example of a competitive inhibitory mechanism. In this case, methanol is converted to harmful formaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase. A high dose of ethanol is used to alleviate the effect of ethanol by binding the active site of alcohol dehydrogenase competitively.
- Methotrexate is a potent competitive inhibitor of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which plays a role in the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines. Methotrexate acts as a structural analog of dihydrofolate, a substrate of dihydrofolate reductase.
Other related notes:
Useful numbers of cell cultures: https://thebiologyislove.com/useful-numbers-for-cell-culture/
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/fxKhnoijuTLTNQXN/?mibextid=oFDknk
Instagram link: https://www.instagram.com/p/C8KQmuAShJd/?igsh=MWloZnZuM3lhajB2ZA==