Table of Contents
Mitosis vs Meiosis is the most important topic to understand in cell biology. This is very important for all life science related competitive exams. Please read the notes and go through the informative diagrams to the end.
Mitosis vs Meiosis: A brief introduction:
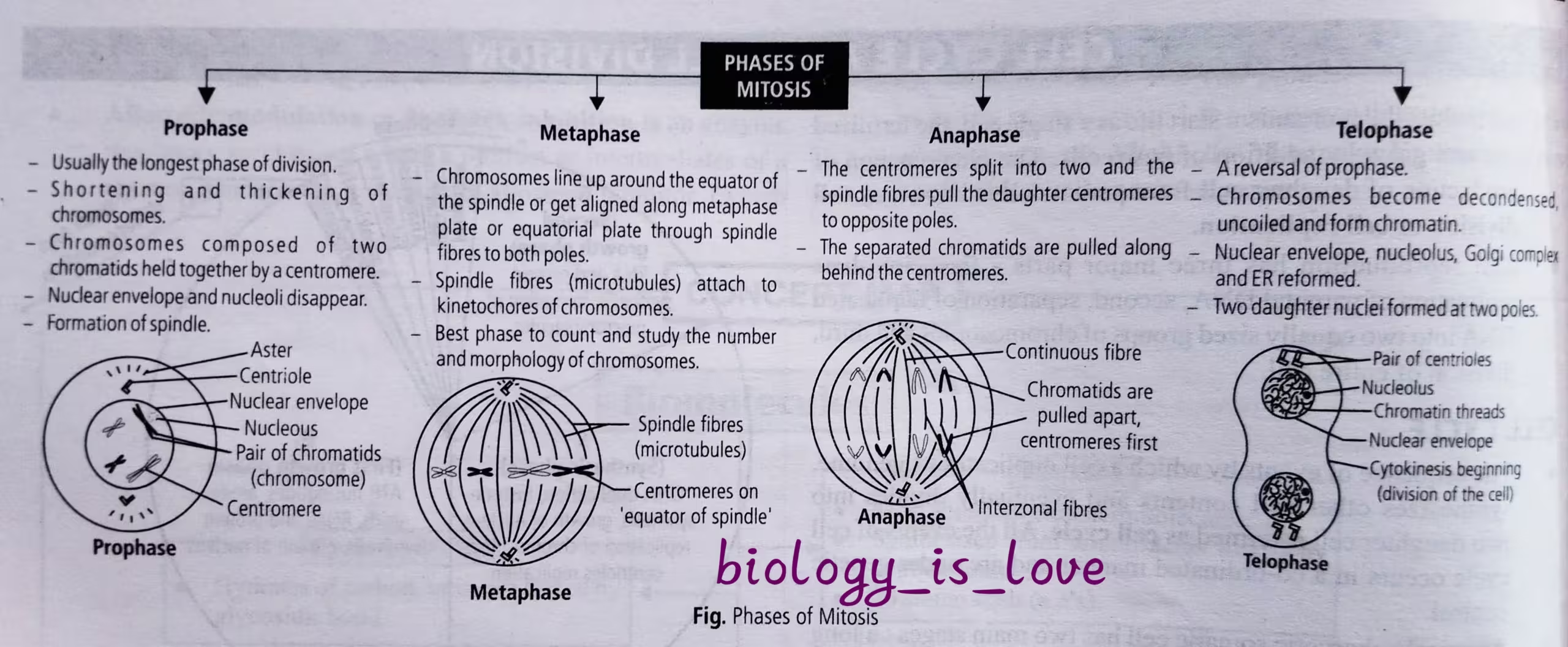
Mitosis
Mitosis involves the exact replication of parent cell followed by its division into two daughters cells which are identical and contain the same numbers of chromosomes as in parent cells.
Invention of Mitosis:
It was first observed by Strassburger (1870) in plant cells and Fleming (1882) in animal cells.
Fleming used the term mitosis (Gk. mitos= thread).
Occurrence:
In plants mitosis occurs in the meristematic cells of root or shoot tip.
Mitosis is divided into four stages as given in the flow chart:
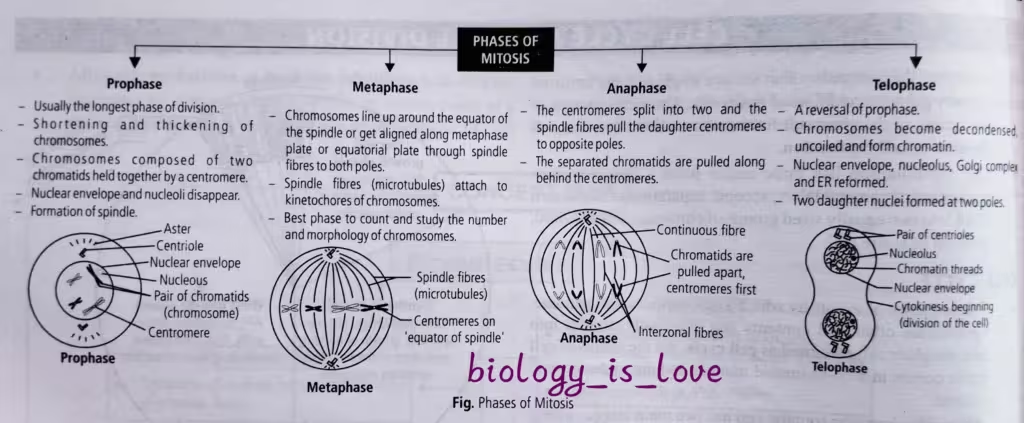
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized kind of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half which results in the production of haploid daughter cells. It ensures the production of haploid phase in the life cycle of sexually reproducing organisms, whereas fertilization restores the diploid phase.
Meiotic events can be grouped into different phases as elaborated in the flow chart below:
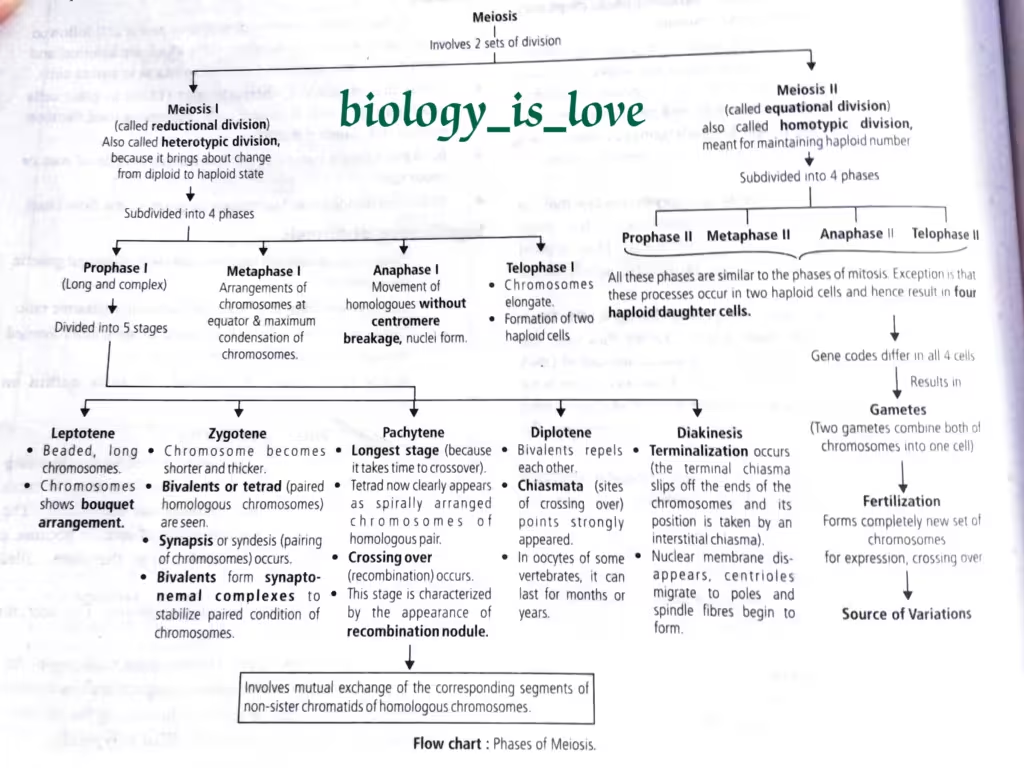
The key features of meiosis is briefly given below:
- Meiosis involves two sequential cycles of nuclear and cell division called meiosis I and meiosis II but have only a single cycle of DNA replication.
- Meiosis I is initiated after the parental chromosomes have replicated to produce identical sister chromatids at S phase.
- Meiosis involves pairing of homologous chromosomes and recombination between them.
- Four haploid cells are formed at the end of meiosis II.
Mitosis vs Meiosis: Significance:
Mitosis:
- Production of diploid daughter cells with identical genetic complement.
- Cell division helps to restore the nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio.
- Old or worn out cells are replaced by new cells formed through mitosis.
- It helps to increase the number of cells within an organism.
Meiosis:
- This Leads to formation of sex cells or gametes capable of engaging in fertilization.
- Meiosis Provides opportunities for new combination of genes to occur in the gametes by two ways – independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over.
- It Switches on the genetic information for the development of gametes and switches off the sporophytic information.
- Chromosomal and gene mutations can take place by irregularities of meiotic divisions.
Mitosis vs Meiosis: A comparative study in the tabulated form:
| The features | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| 1. The numbers of cell divisions | only once | There are two cell divisions- meiosis I and meiosis II. |
| 2. Occurrence | somatic cells | germ cells |
| 3. DNA replication takes place | during interphase | during interphase I but not in during interphase II. |
| 4. Duration of prophase | short, usually takes few hours. | comparatively longer and may take days. |
| 5. Synapsis of homologous chromosomes | Absent | in prophase I |
| 6. Crossing over | Absent | in prophase I |
| 7. Centromeric division | takes place in anaphase | does not take place in anaphase I but observed in anaphase II. |
| 8. Anaphasic chromosomes | single stranded | double stranded in anaphase I and single stranded in anaphase II. |
| 9. The chromosome number | remains constant at the end of the mitosis | reduced from the diploid to the haploid |
| 10. Daughter cells | identical to that of parent cells | differs from that of parent cells. The chromosomes of the daughter cell are a mixture of the maternal and the paternal genes. |
| 11. Multiplication of cells | present | absent |
| 12. Takes part in | in healing and repair | in the formation of meiospores or gametes and maintenance of chromosome number of the race. |
The schematic representation of different phases of meiosis in animal cell:
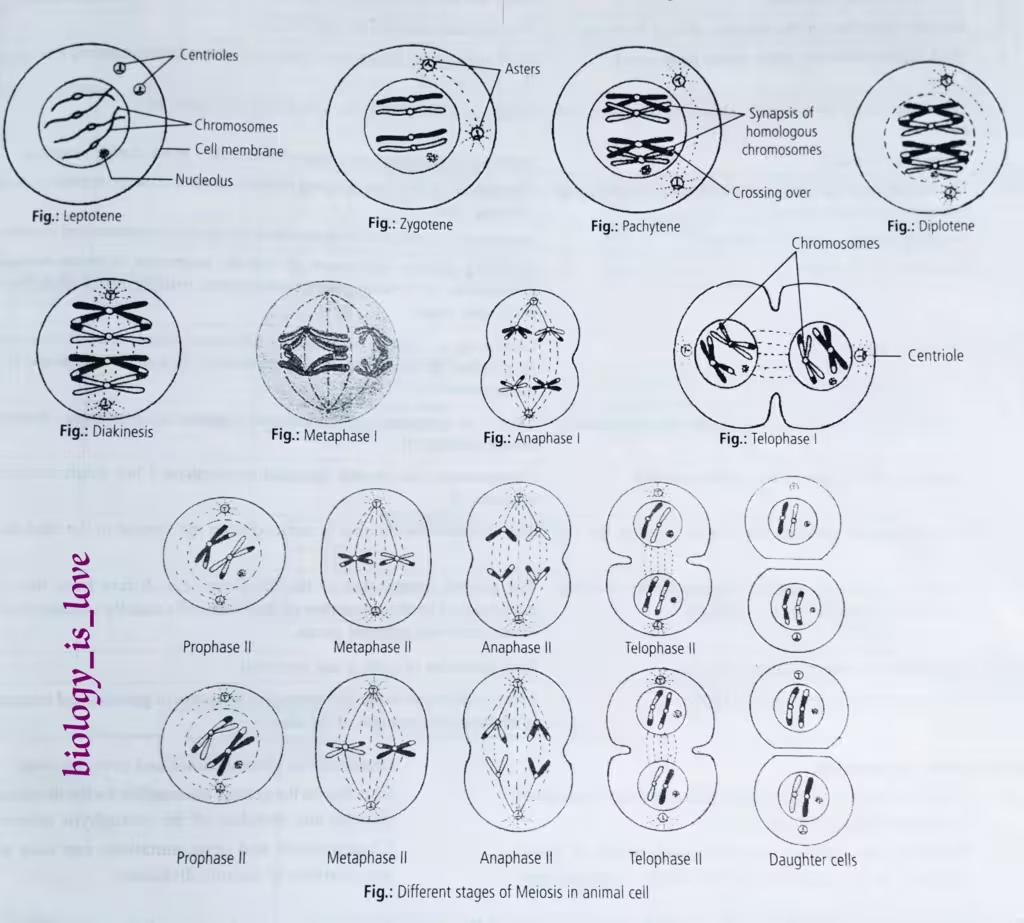
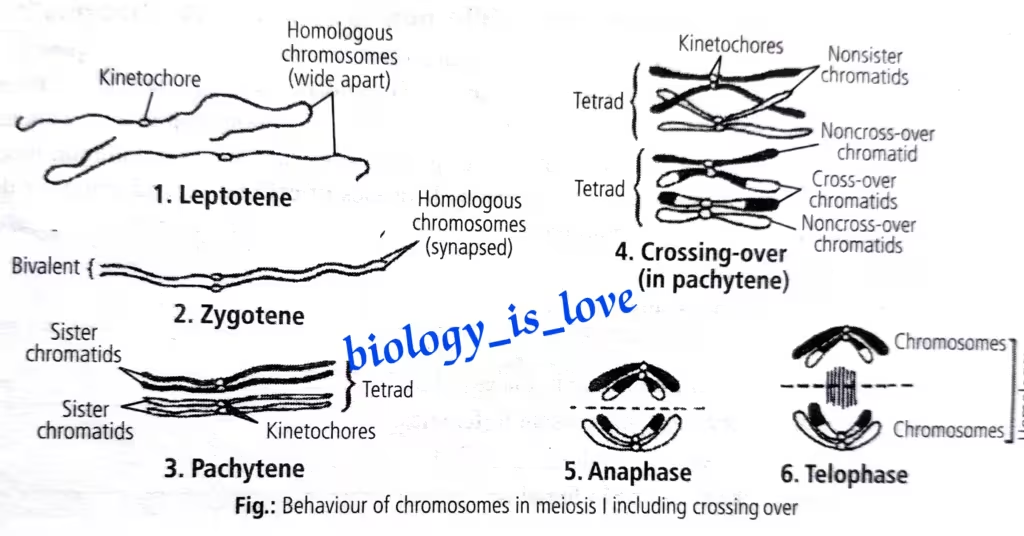
The schematic representation of behavior of chromosomes of chromosomes in meiosis I including crossing over:
Other related notes:
- Cell cycle checkpoints: https://thebiologyislove.com/cell-cycle-checkpoints/
- Prophase I: https://thebiologyislove.com/prophase-1/
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/ZKGEbpPVoQgbdF5d/?mibextid=oFDknk
Instagram link: https://www.instagram.com/reel/C8hgbqvS_hd/?igsh=d2JhZ2phOXppM2tv