Table of Contents
5′ capping is one of the methods of processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA. Eukaryotic mRNA has a unique enzymatically appended cap structure consisting of 7- methylguanosine residue joined via a 5′-5′ triphosphate bridge. During transcription, 7- methylguanosine is added to the 5′ end of nascent mRNA.
The steps of 5′ capping:
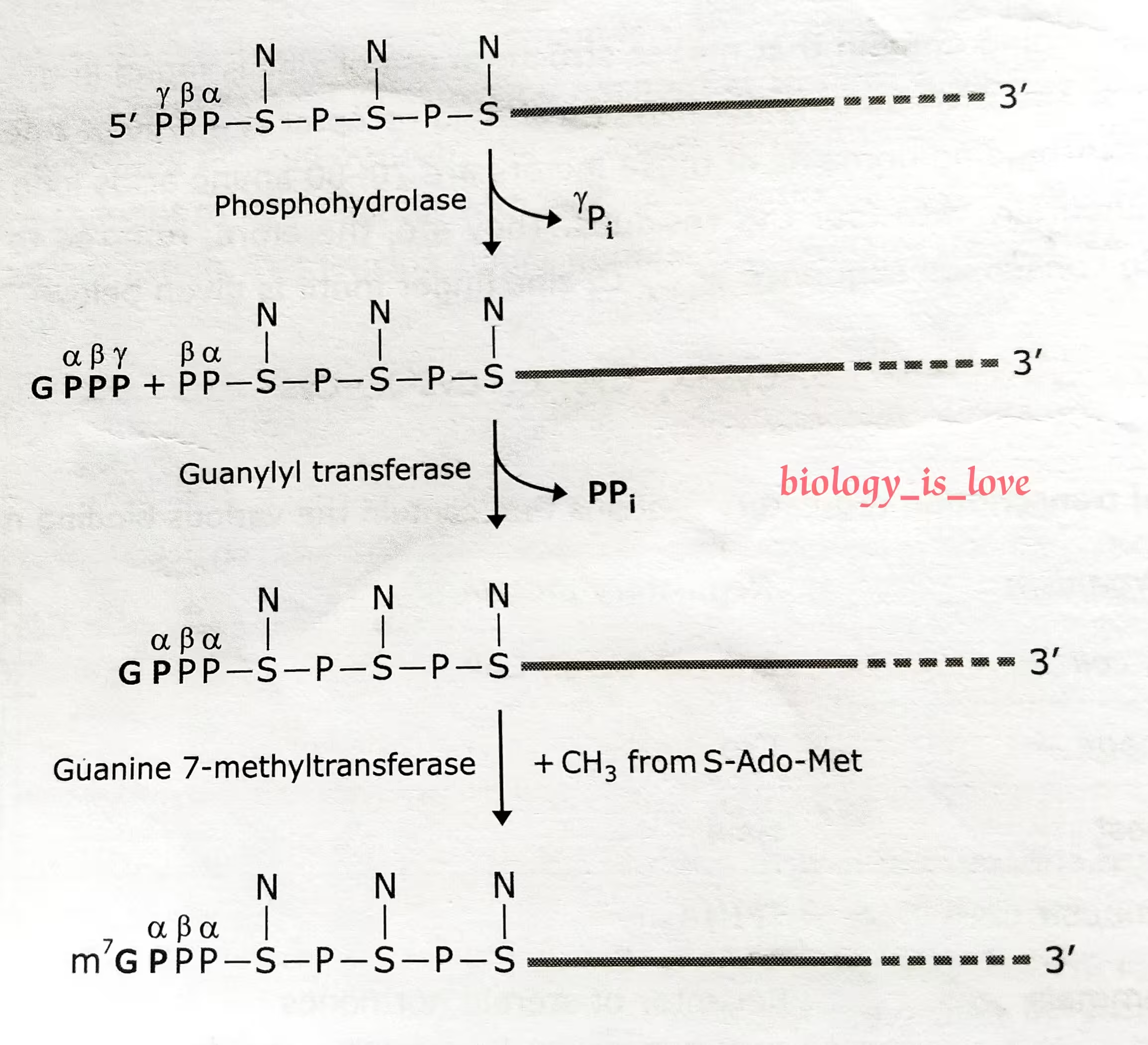
- The initial step in RNA 5′ capping is catalyzed by a dimeric capping enzyme, which associates with the phosphorylated carboxyl-terminal tail domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II.
- One subunit of capping enzyme removes the γ-phosphate from the 5′ end of the nascent RNA emerging from the surface of an RNA polymerase II.
- The other subunit transfers the GMP moiety from GTP to the 5′-diphosphate of the nascent transcript, generating the guanosine 5′-5′-triphosphate structure.
- In the final steps, separate enzymed transfer methyl groups from S-adenosylmethionine to the N7 position of the guanine at the 5′ end of the nascent RNA.
- If the mRNA has a methyl group on N7 position of the guanine at the 5′ end, then it is called cap 0.
The schematic representation of the process of 5′ capping:
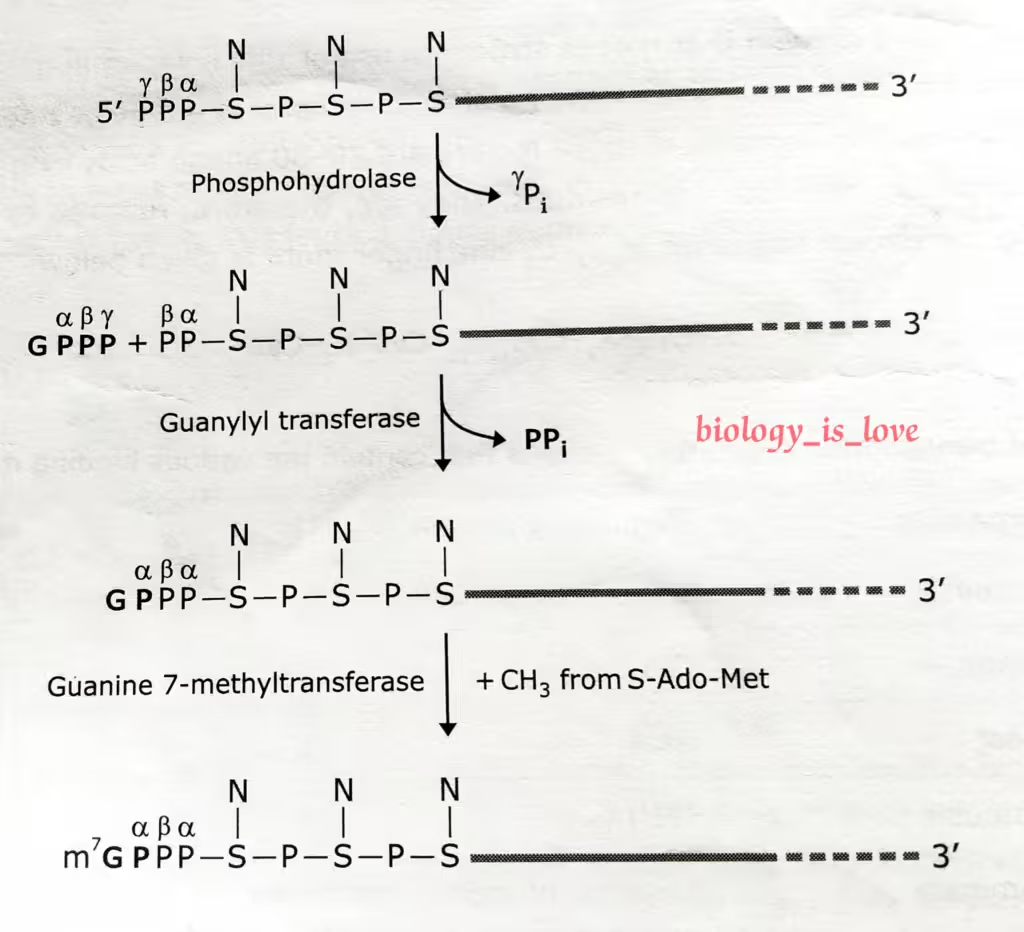
The description of the above diagram:
The reactions that cap the 5′ end of each RNA molecules synthesized by RNA polymerase II. The final cap contains a novel 5′-to-5′ linkage between the positively charged 7-methyl G residue and the 5′ end of the RNA transcript.
The letter N represents any one of the four ribonucleotides, although the nucleotide that starts an RNA chain is usually a purine.
Occurrence:
- The step of cap 0 is the first methylation step and it is occurred in all eukaryotes.
- In some higher eukaryotes, methyl group addition also occurs at second base.
- But this happens only when the position is occupied by adenine. The reaction involves addition at the N6 position.
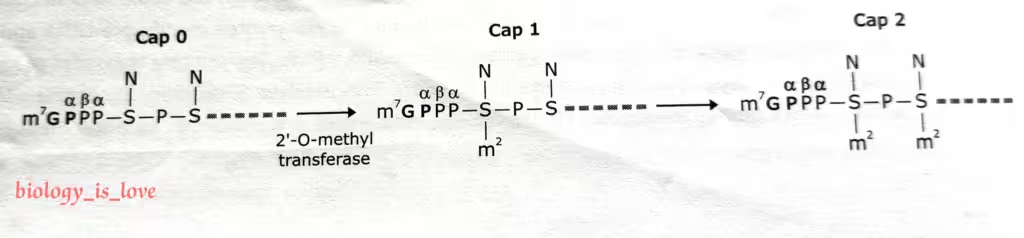
The formation of cap 0, cap 1 and cap 2:
- The mRNA has a methyl group on N7 position of the guanine at the 5′ end, then it is called cap 0.
- In some species, a methyl group is added to the second as well as third nucleoside of the capped mRNA.
- mRNA with methyl groups on the N7 position of the guanine and the 2′-OH position of the second nucleotide at the 5′ end is known as cap 1.
- This is the predominant cap in multicellular organisms. Similarly, if methyl group is present at both second and third nucleoside then it is referred to as cap 2.
Function of the process 5′ capping:
- Protection of mRNA from degradation.
- Transport of the mRNA from nucleus to cytoplasm.
- Binding of ribosome with mRNA.
Other related notes:
- DNA binding motifs: https://thebiologyislove.com/dna-binding-motifs/
- Base excision repair vs Nucleotide excision repair: https://thebiologyislove.com/base-excision-repair-vs-nucleotide-excision-repair/
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/share/p/vtZu91u7fnQUJog6/?mibextid=oFDknk
Instagram link: